Research Question and Findings
RQ: Do the developer perception of quality improvement align with the quantitative assessment of code quality?
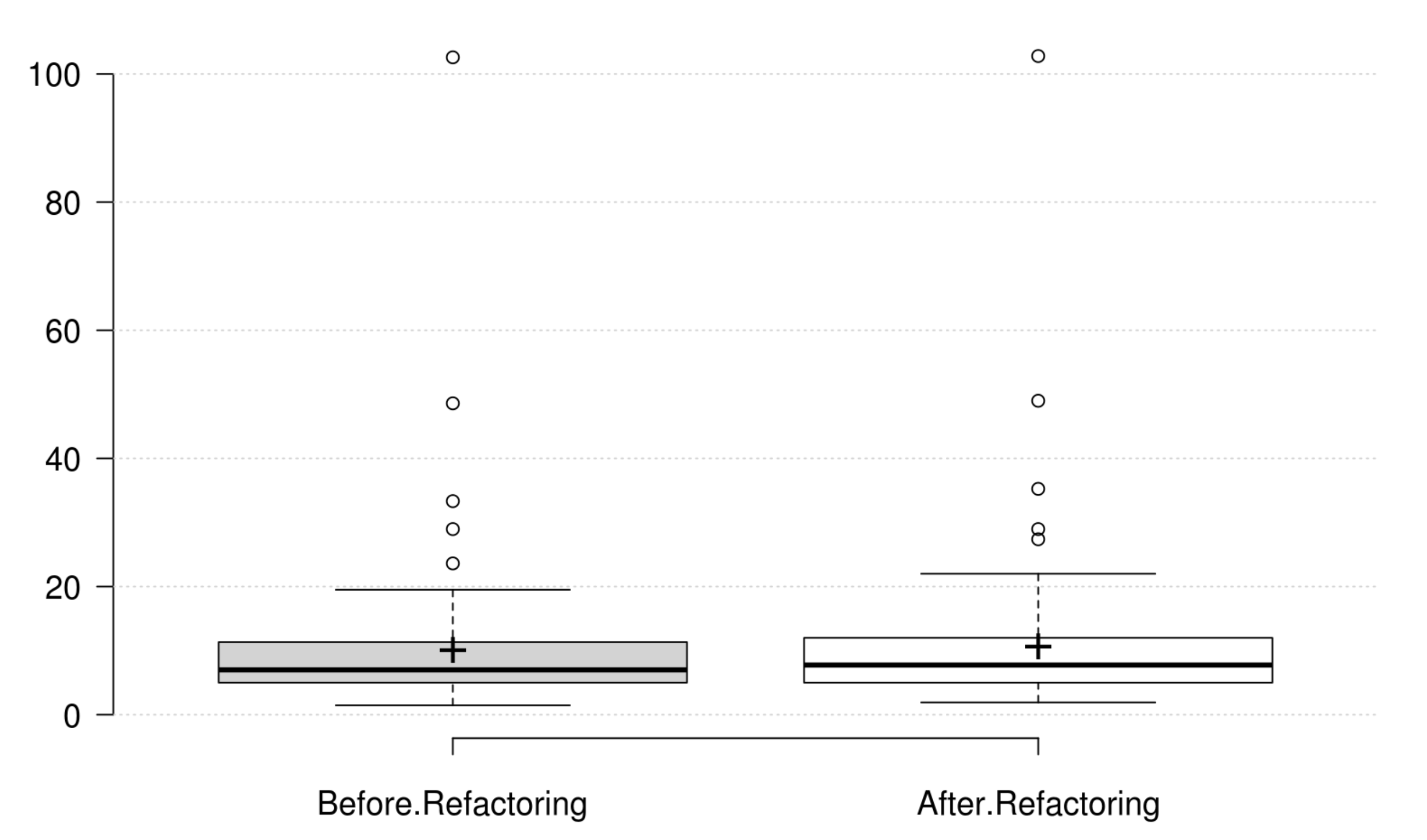
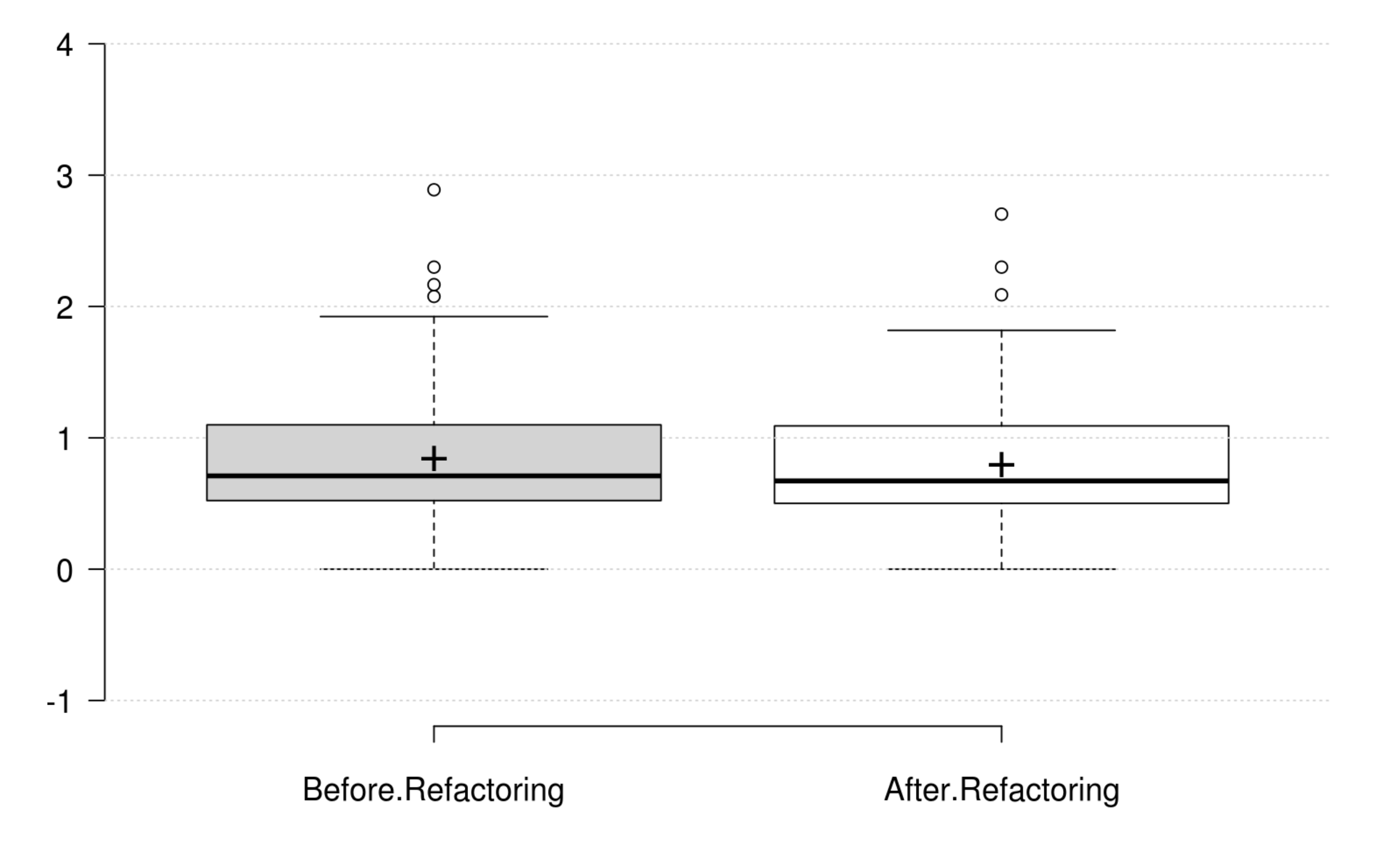
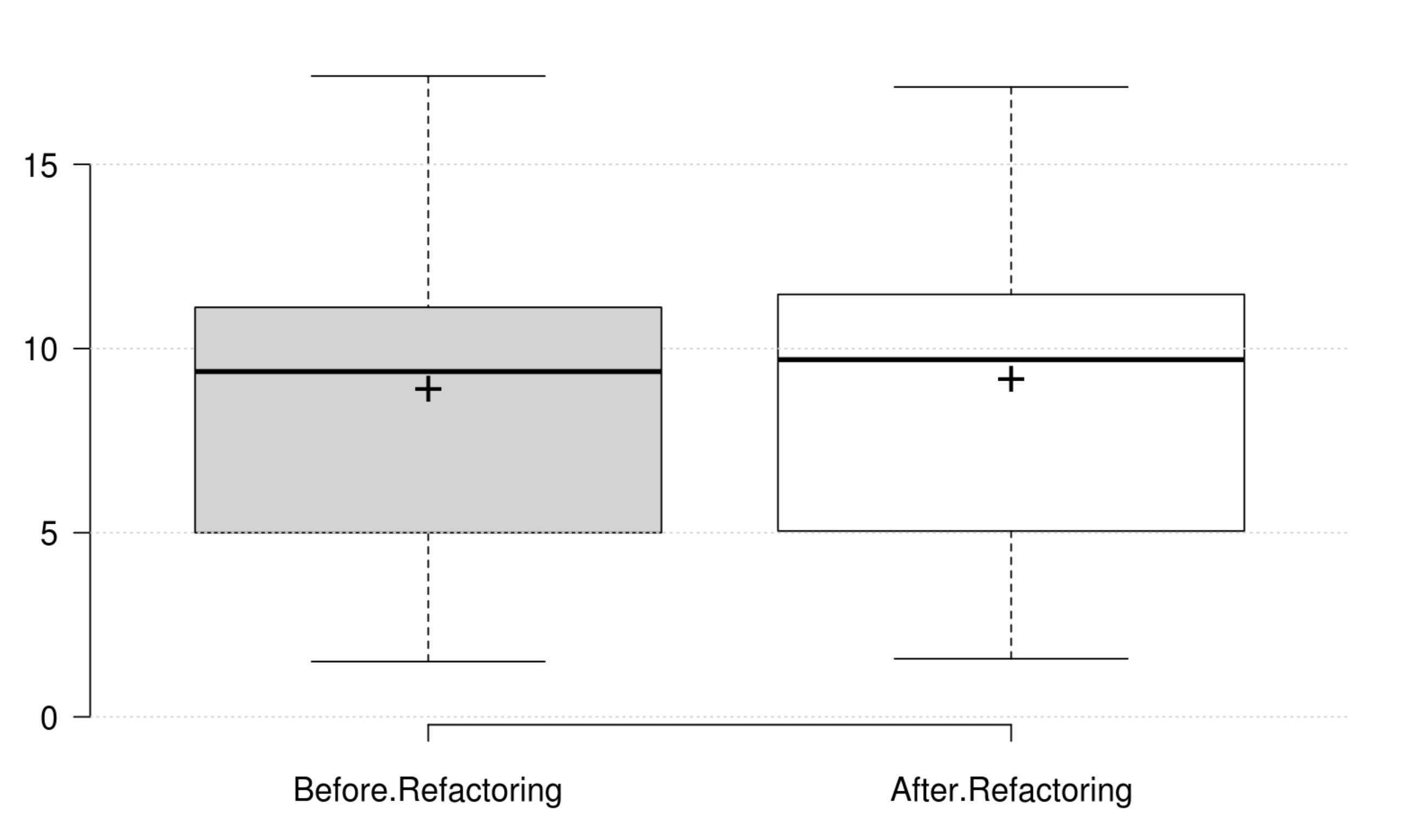
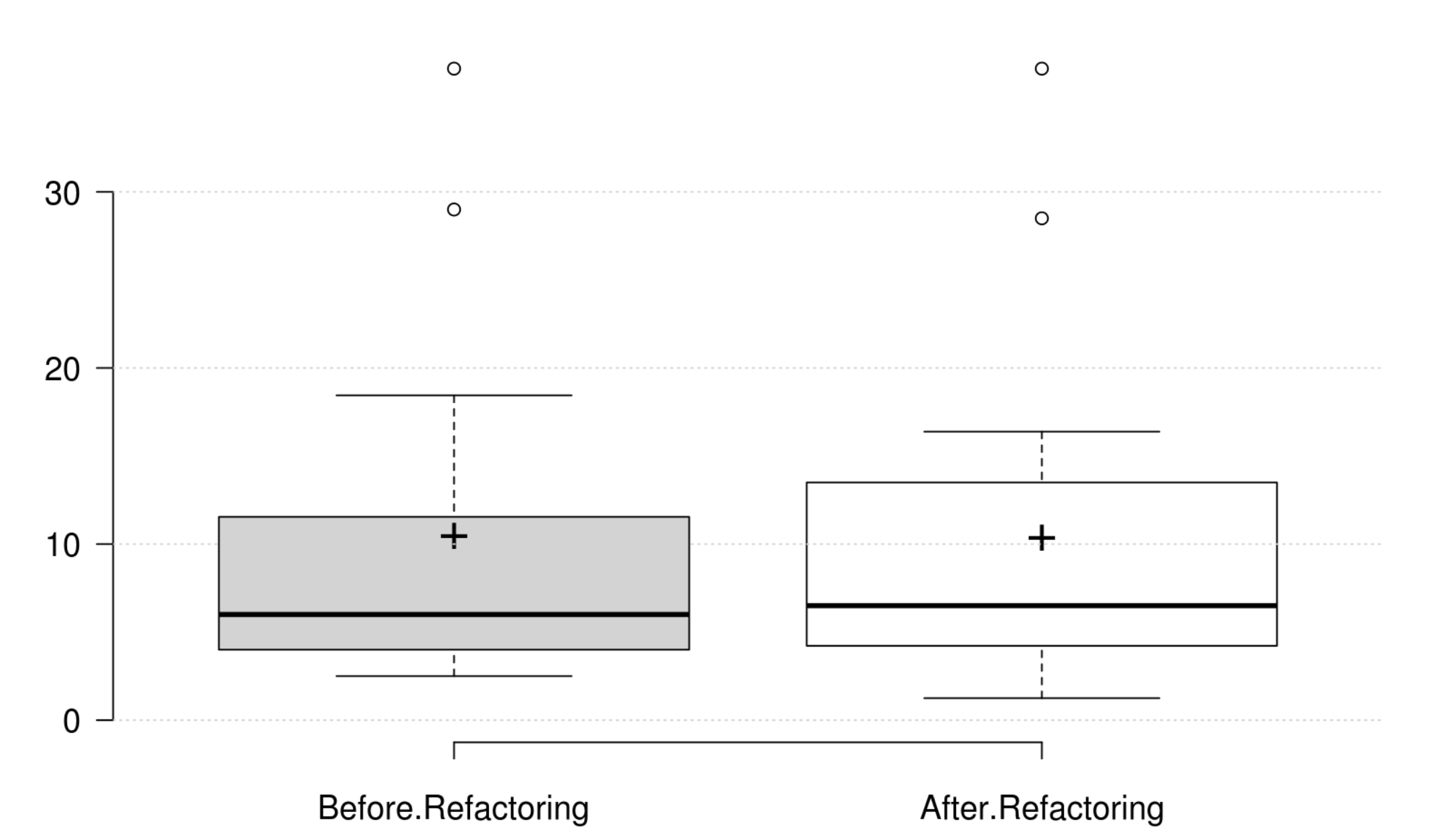
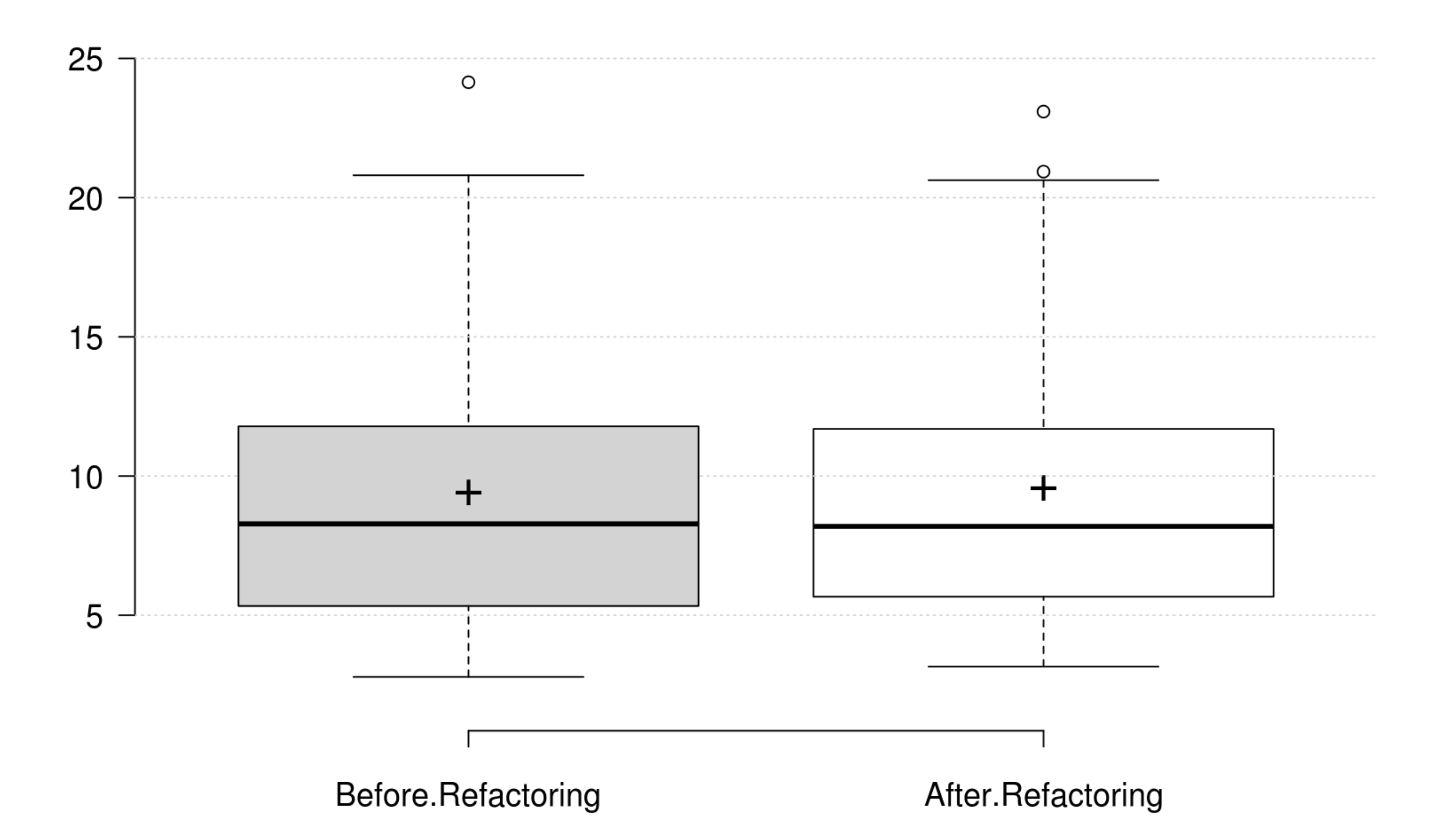
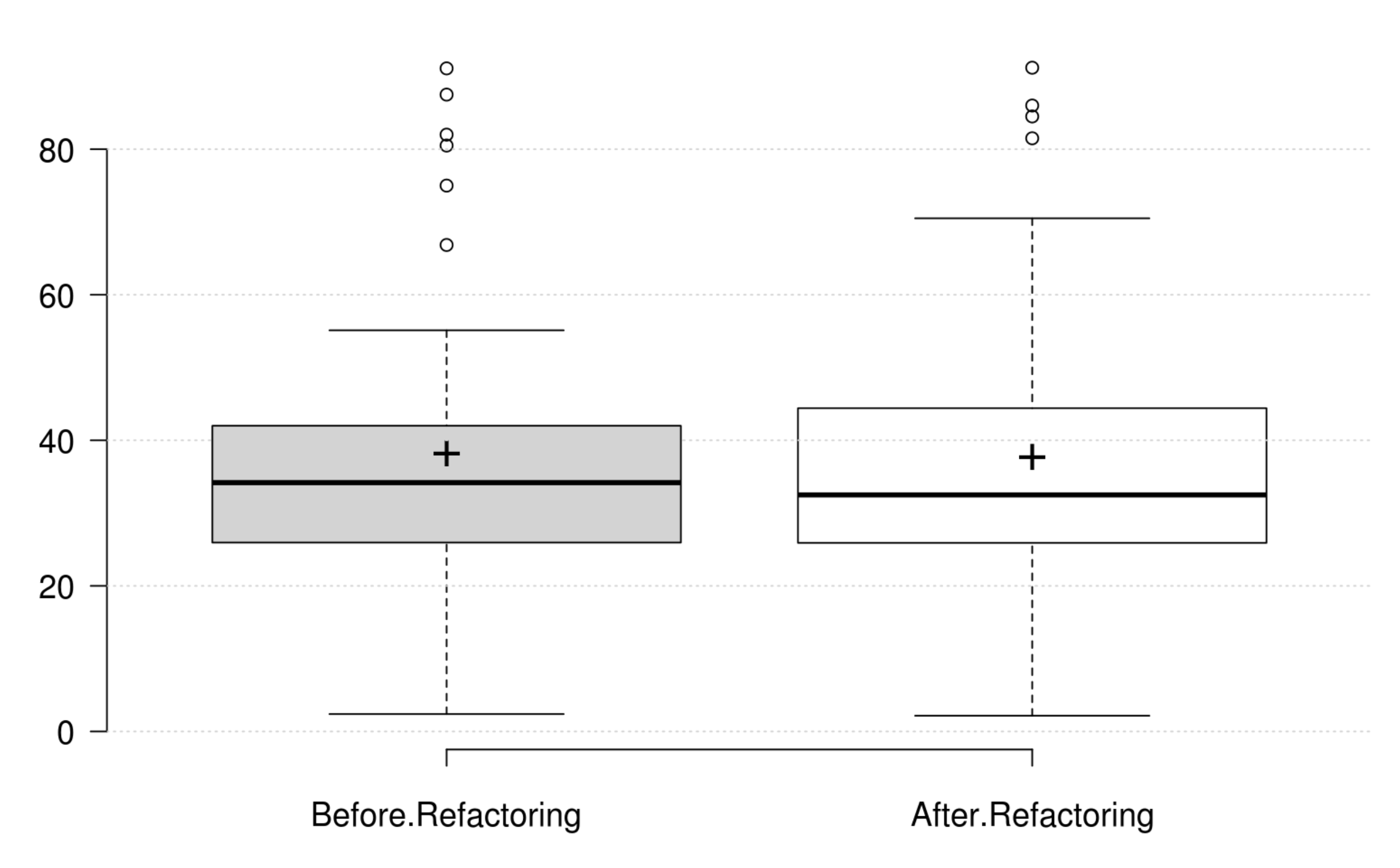
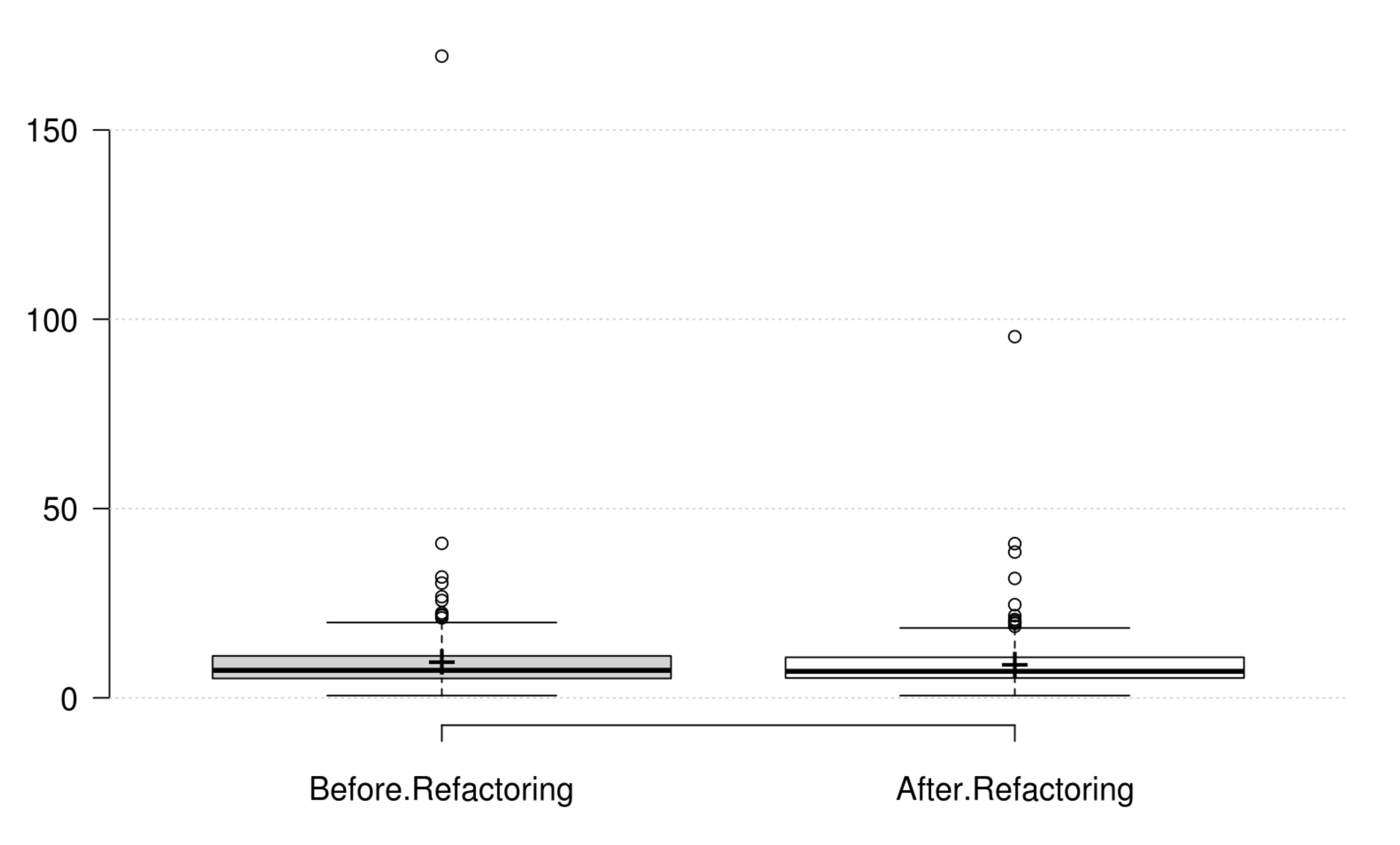
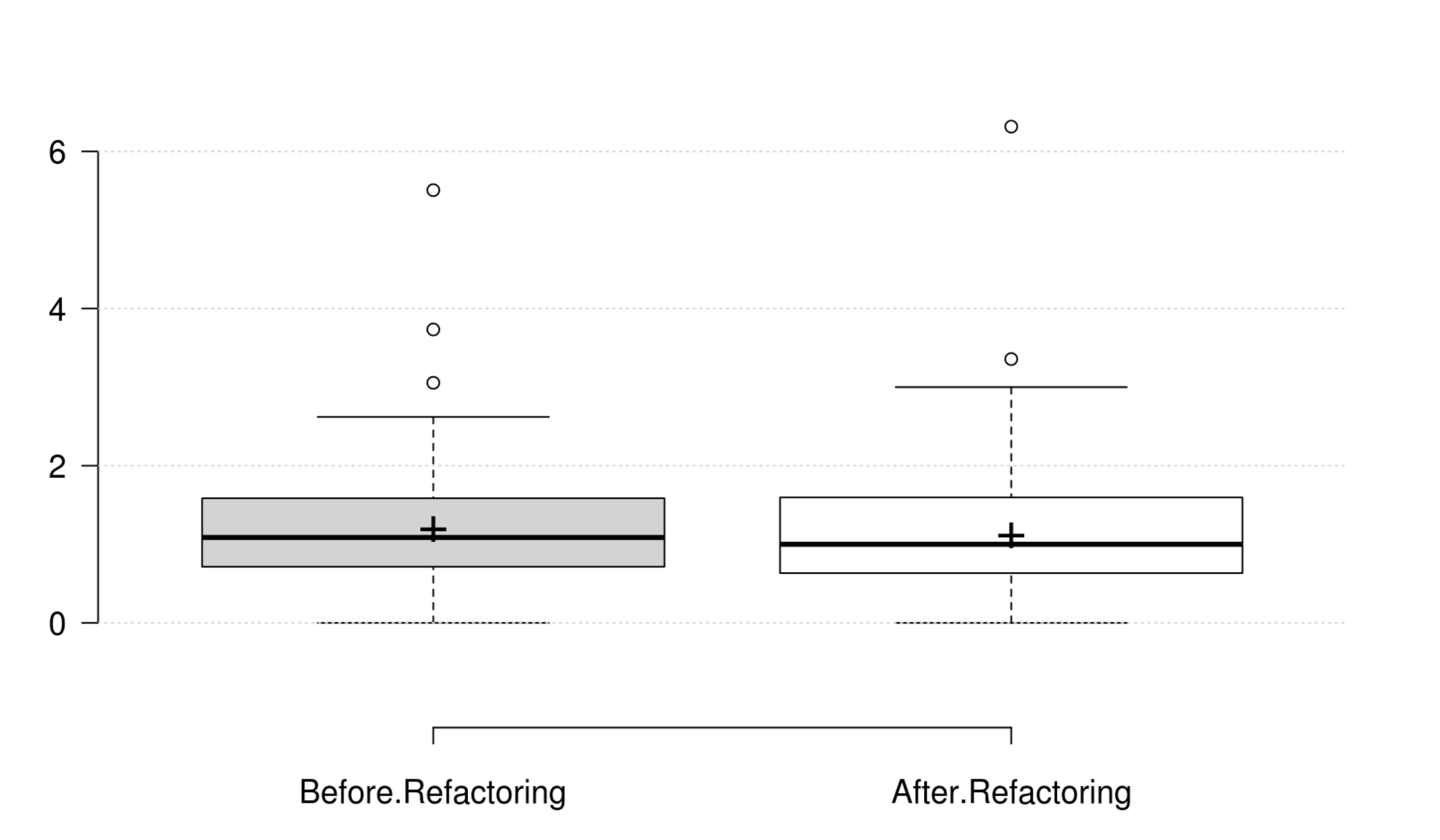
Cohesion: The normalized LCOM metric does not onlyrepresent a good replacement to the original LCOM, but also represents the cohesion quality attribute. Its positive variation is in line with the developer's intention in improving cohesion.
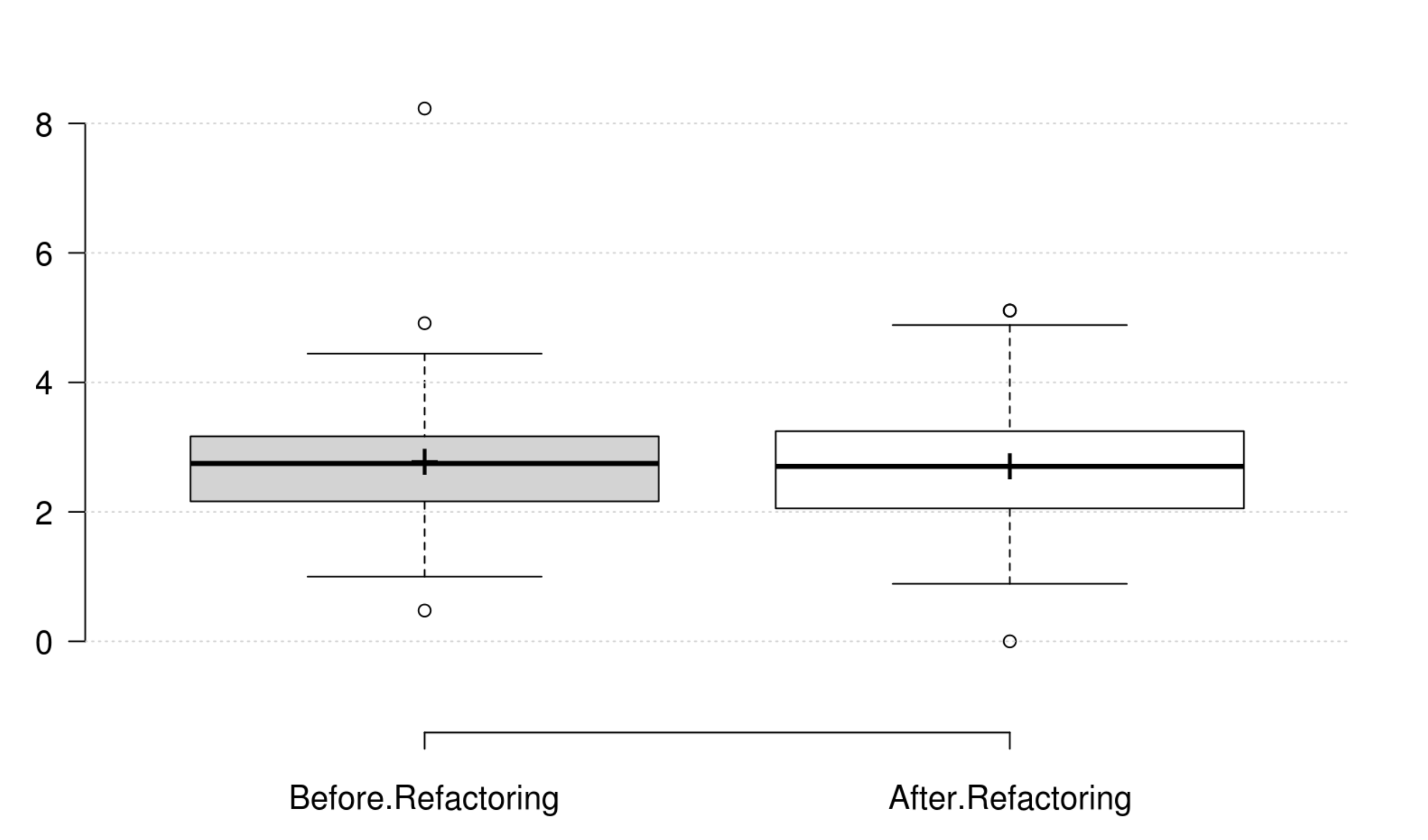
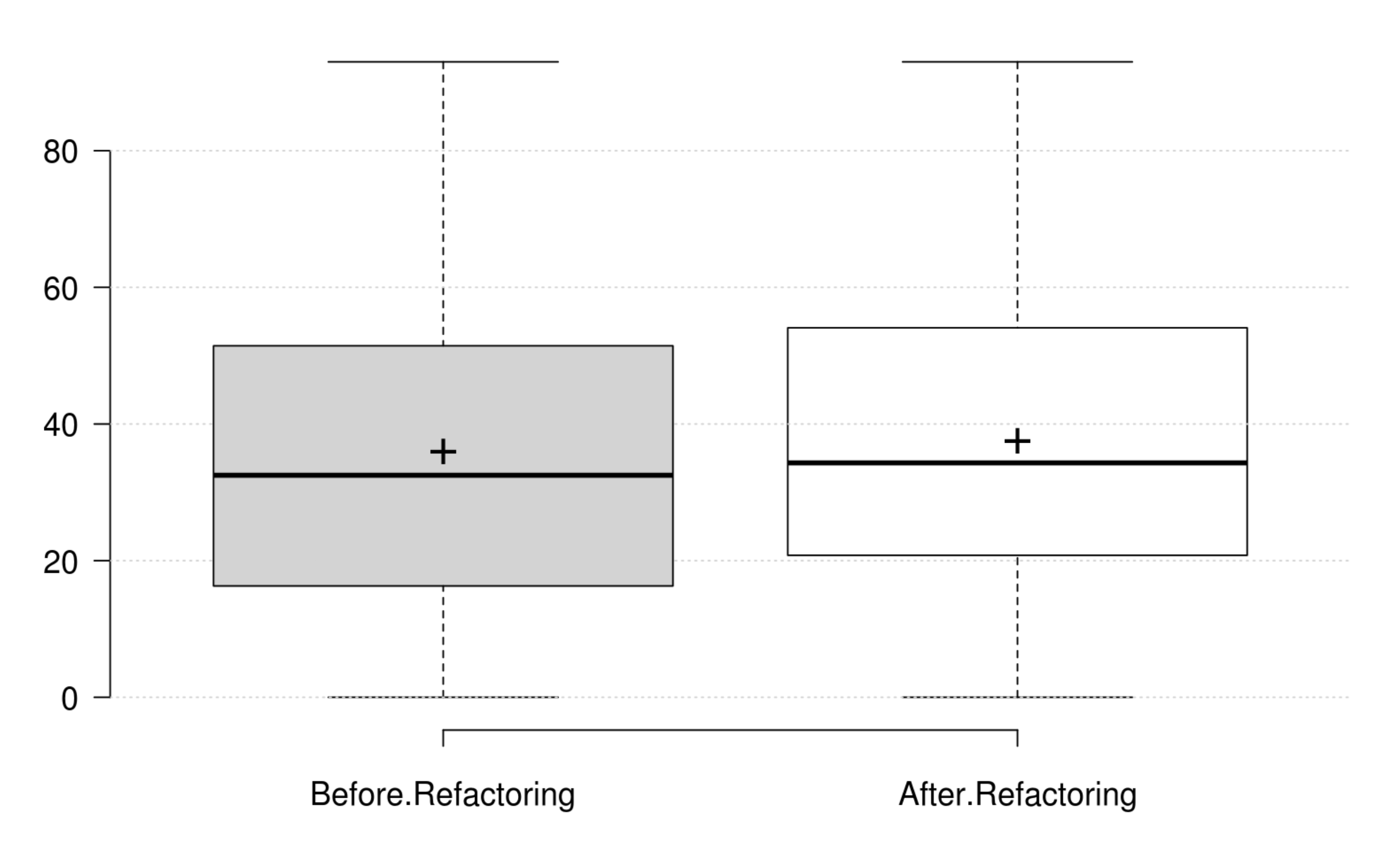
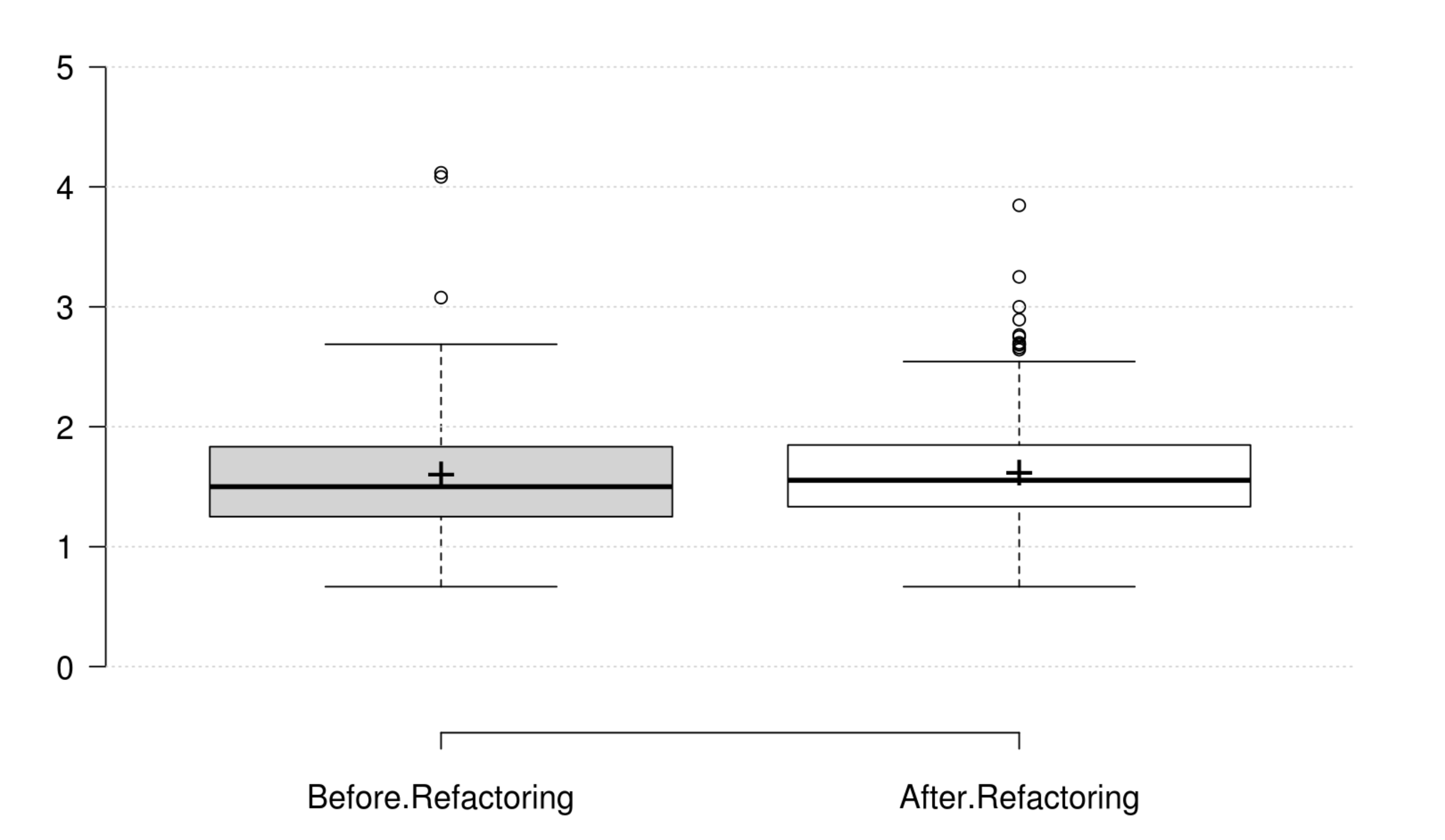
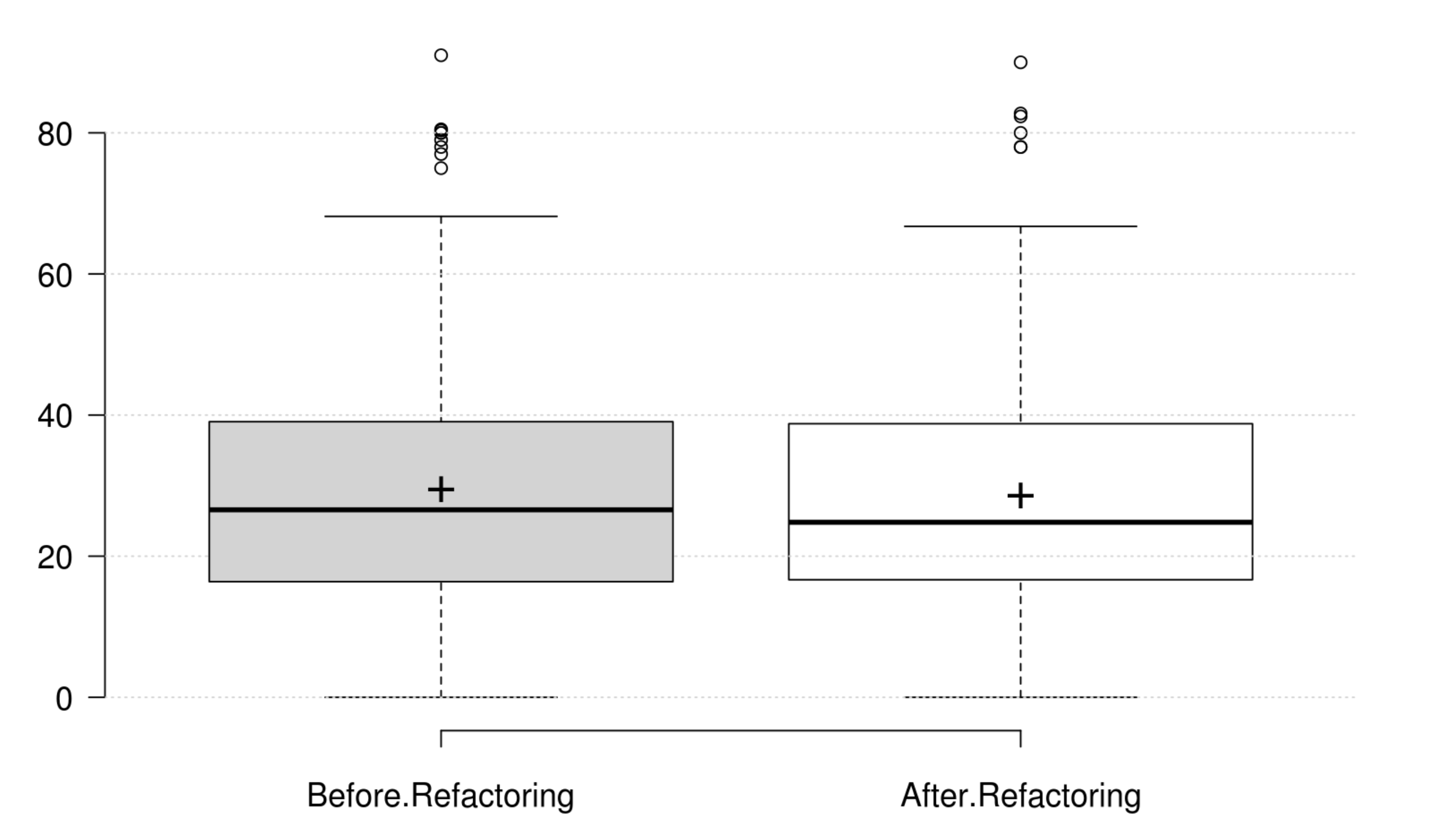
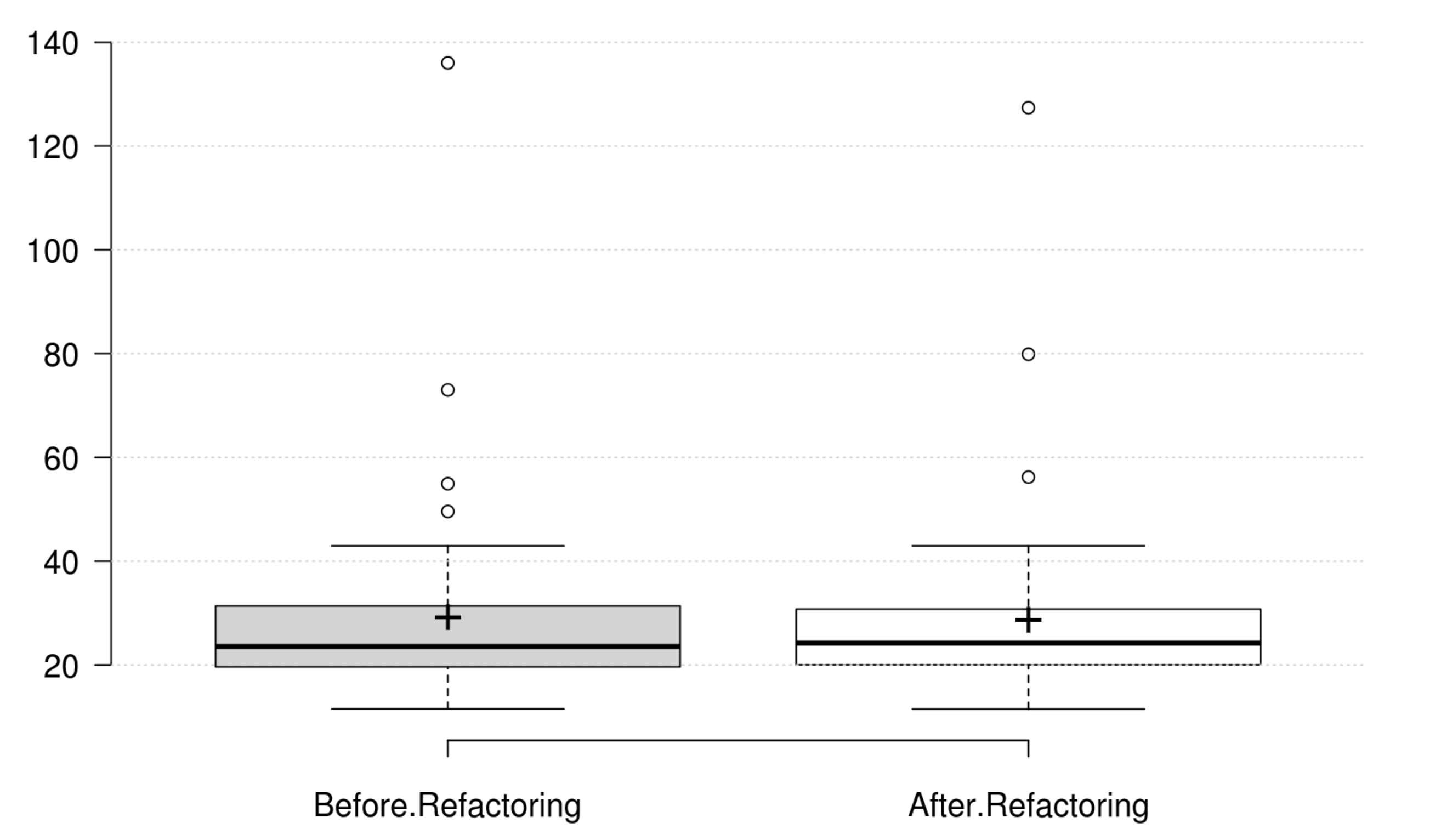
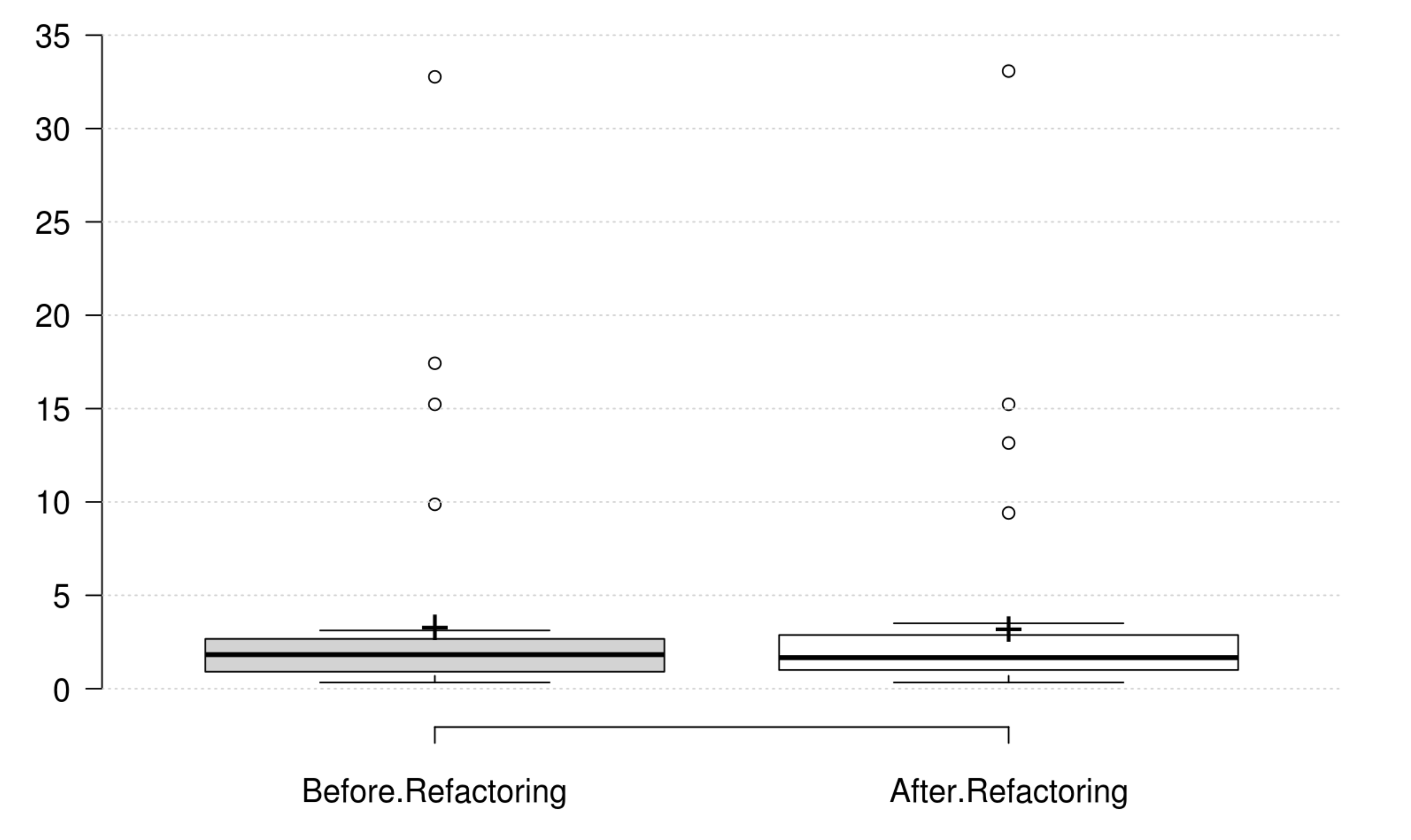
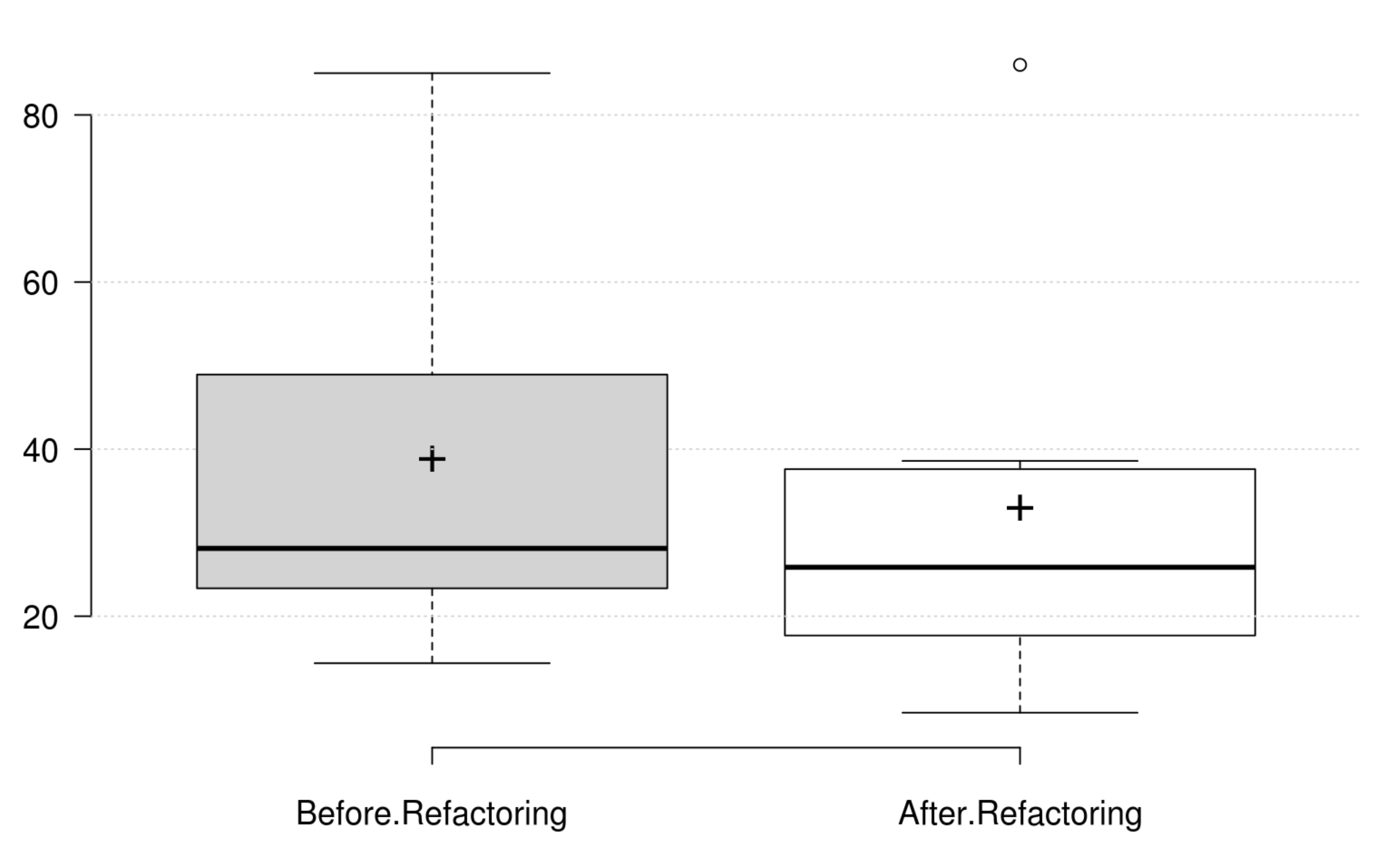
Coupling: CBO, FANIN and FANOUT generally decrease as developer intends to improve coupling. However, only CBO and FANOUT variation is significant. RFC exhibits an opposite variation to coupling, but it is not statistically significant. Finally, at least one metric has a significant positive variation which matches the developer's perception of improving coupling.
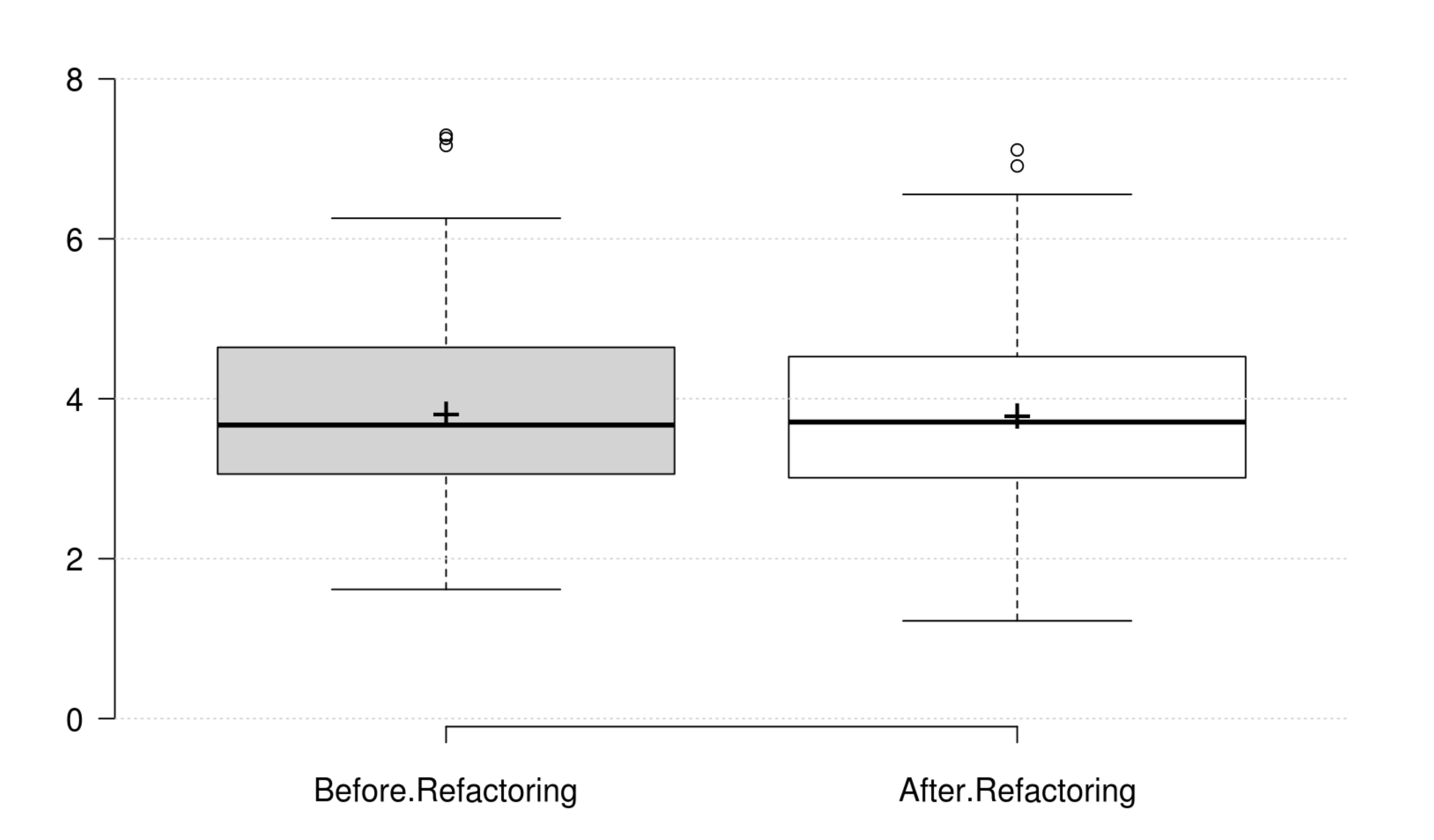
Complexity: CC, WMC, Evg, NPATH, and MaxNest generally decrease as developer intends to improve complexity, and all their variation is significant. Furthermore, our empirical investigation discards RFC from being an indicator for complexity. Finally, at least one metric has a significant positive variation which matches the developer's perception of improving complexity.
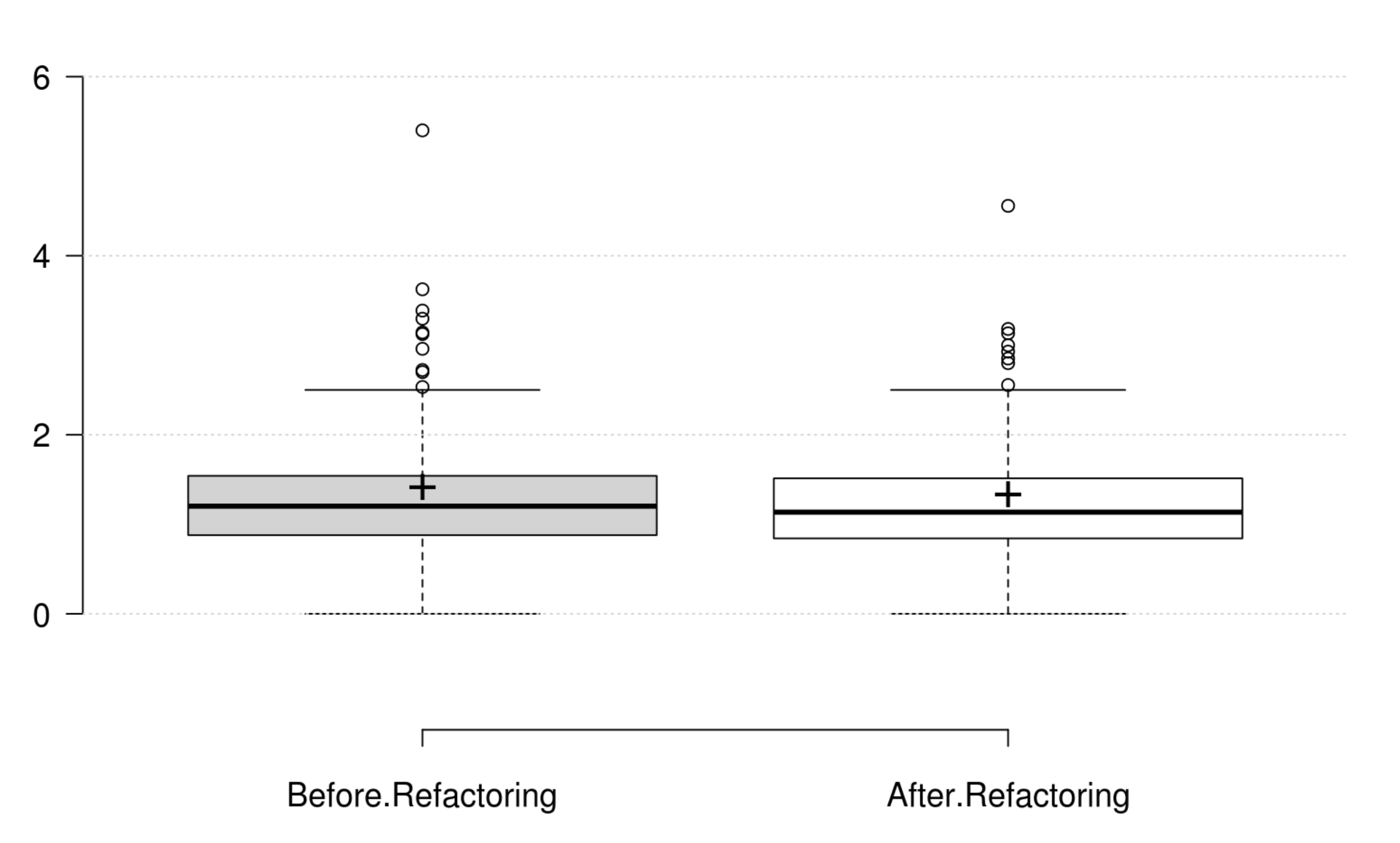
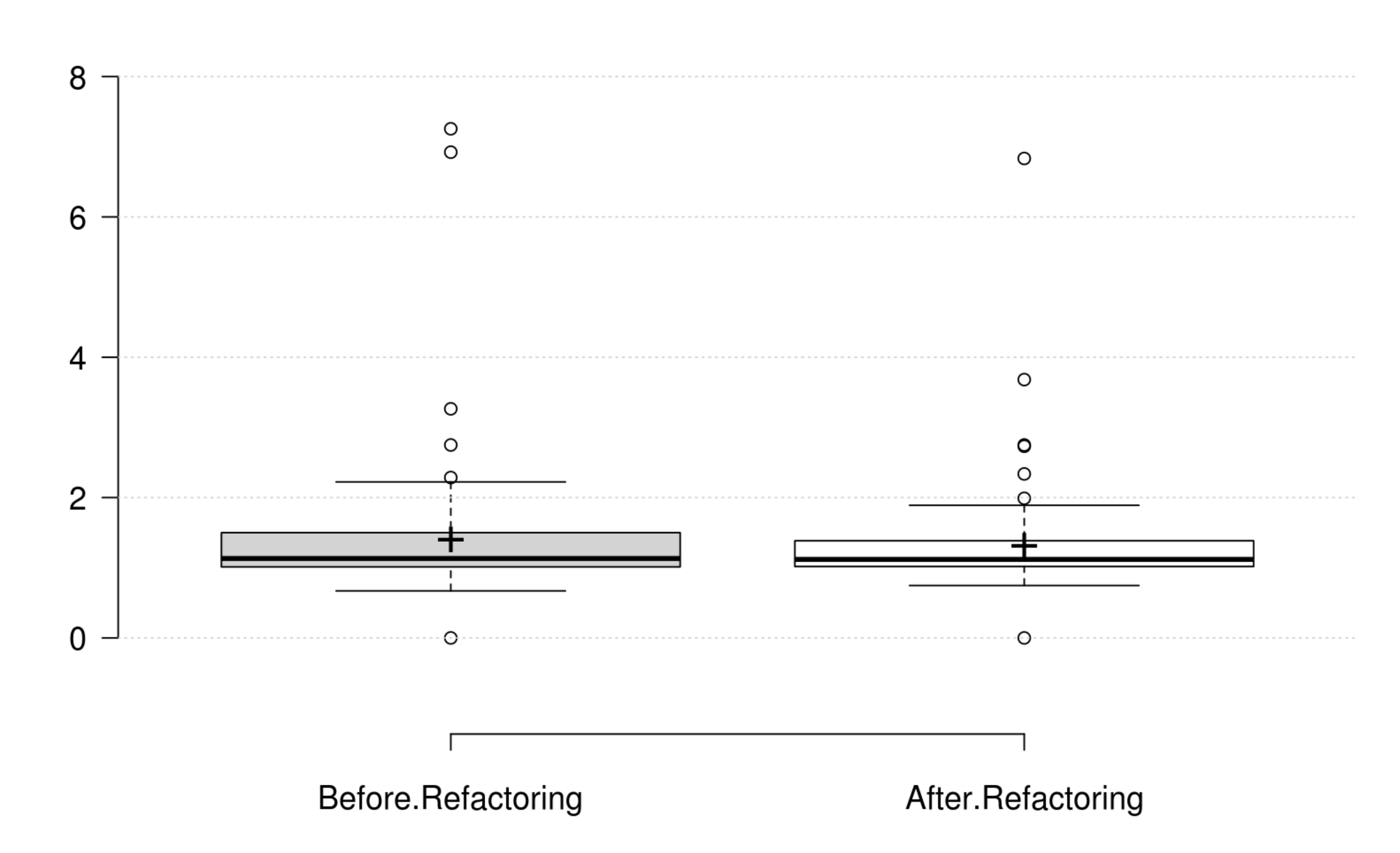
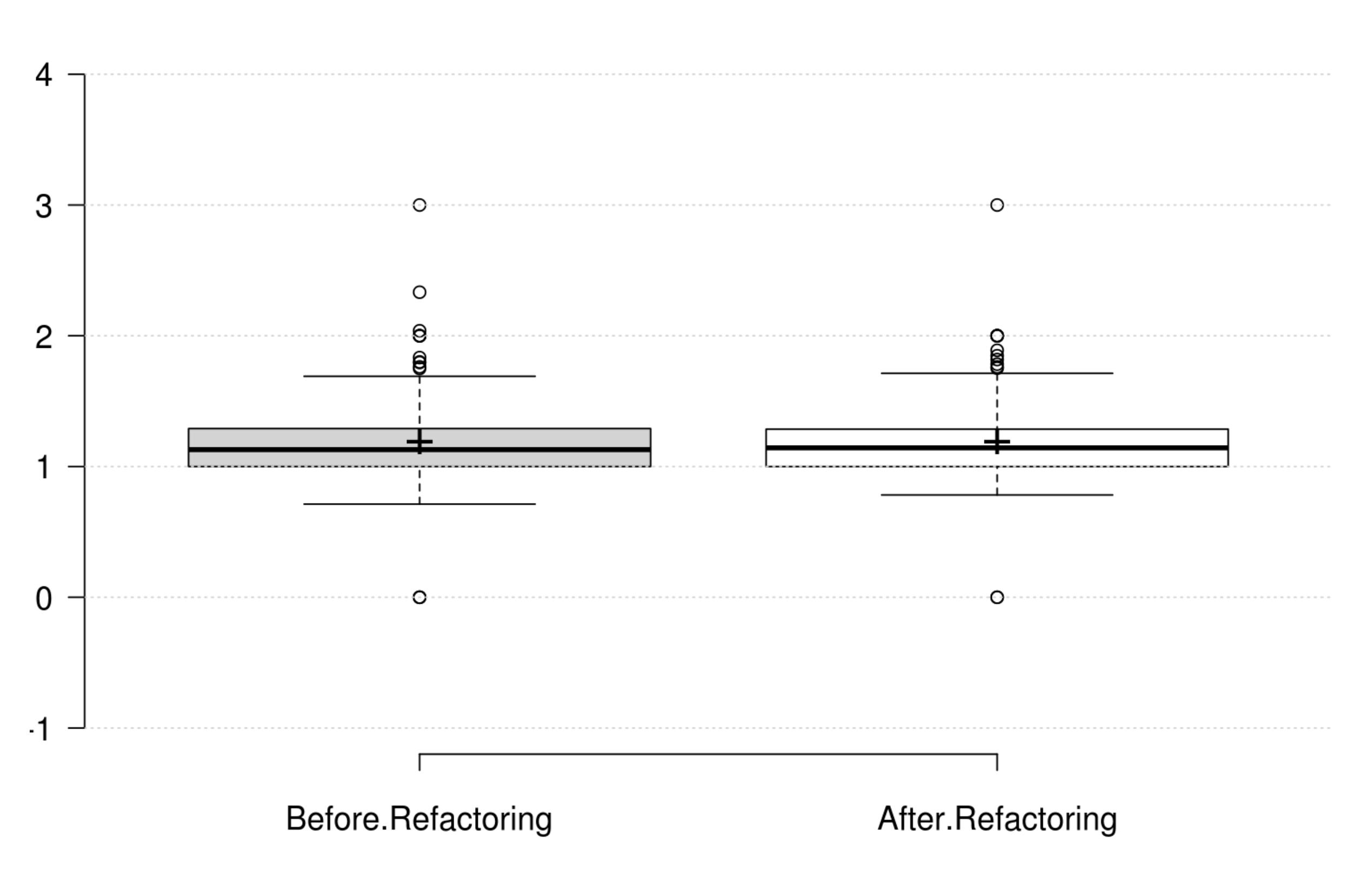
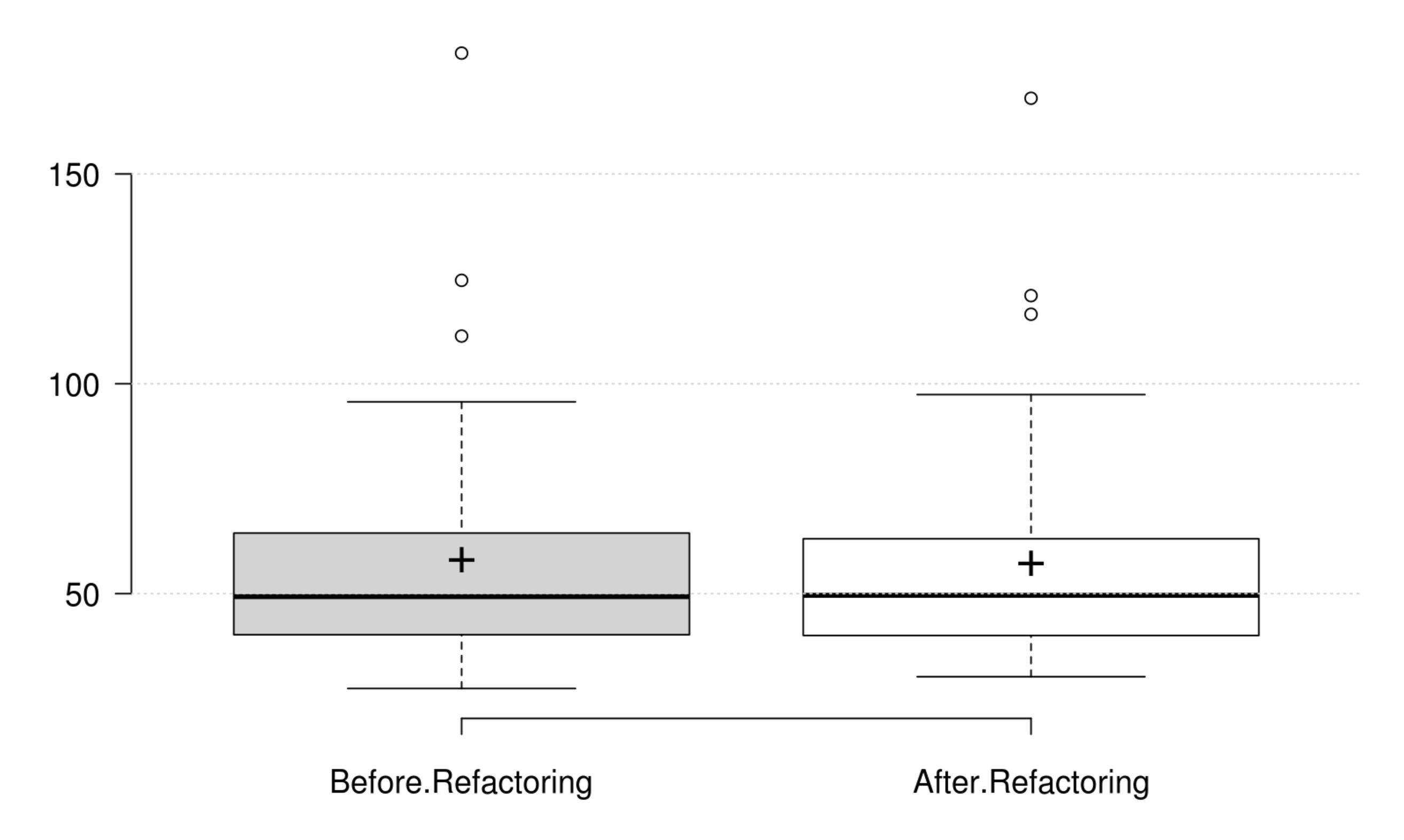
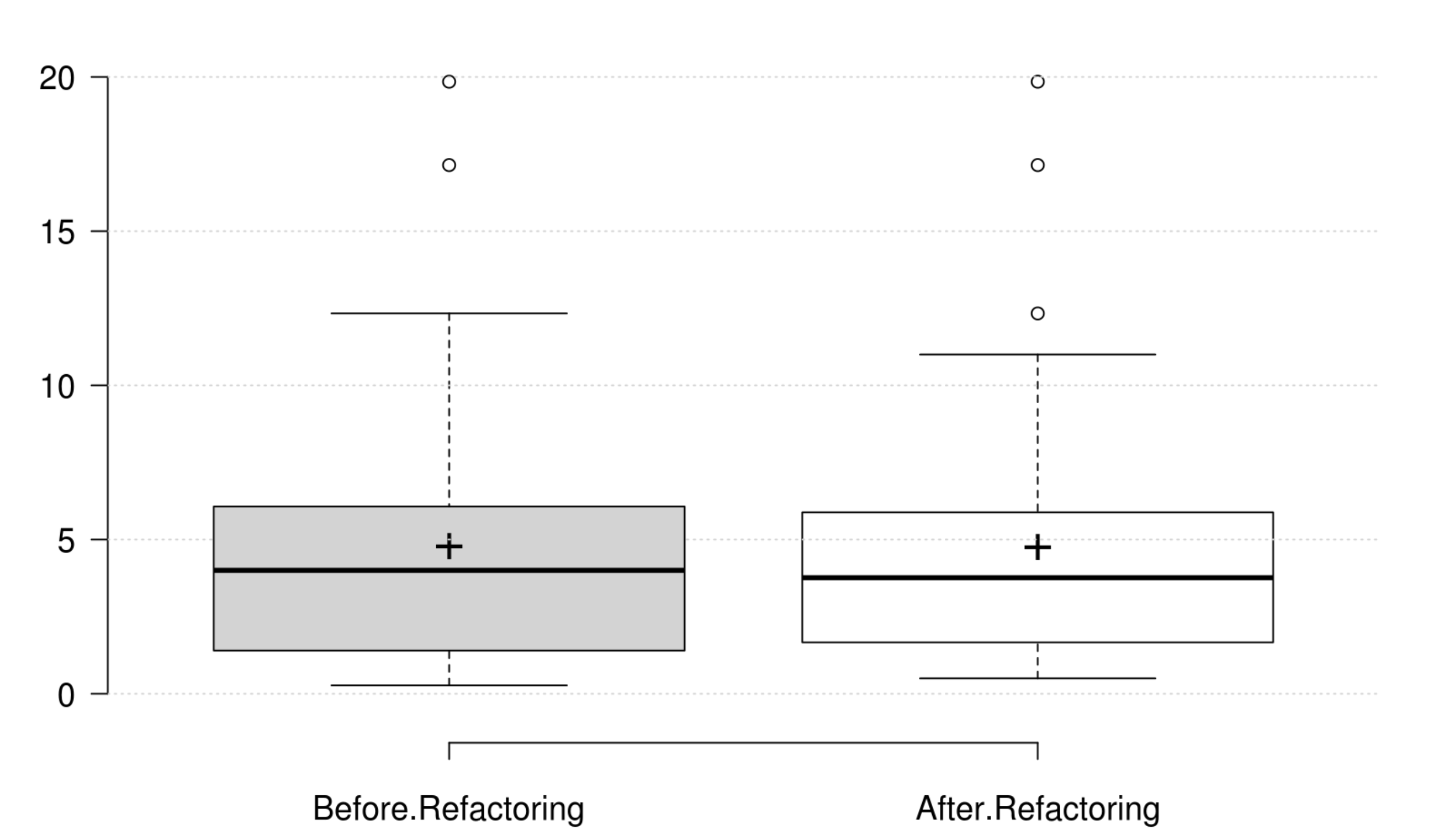
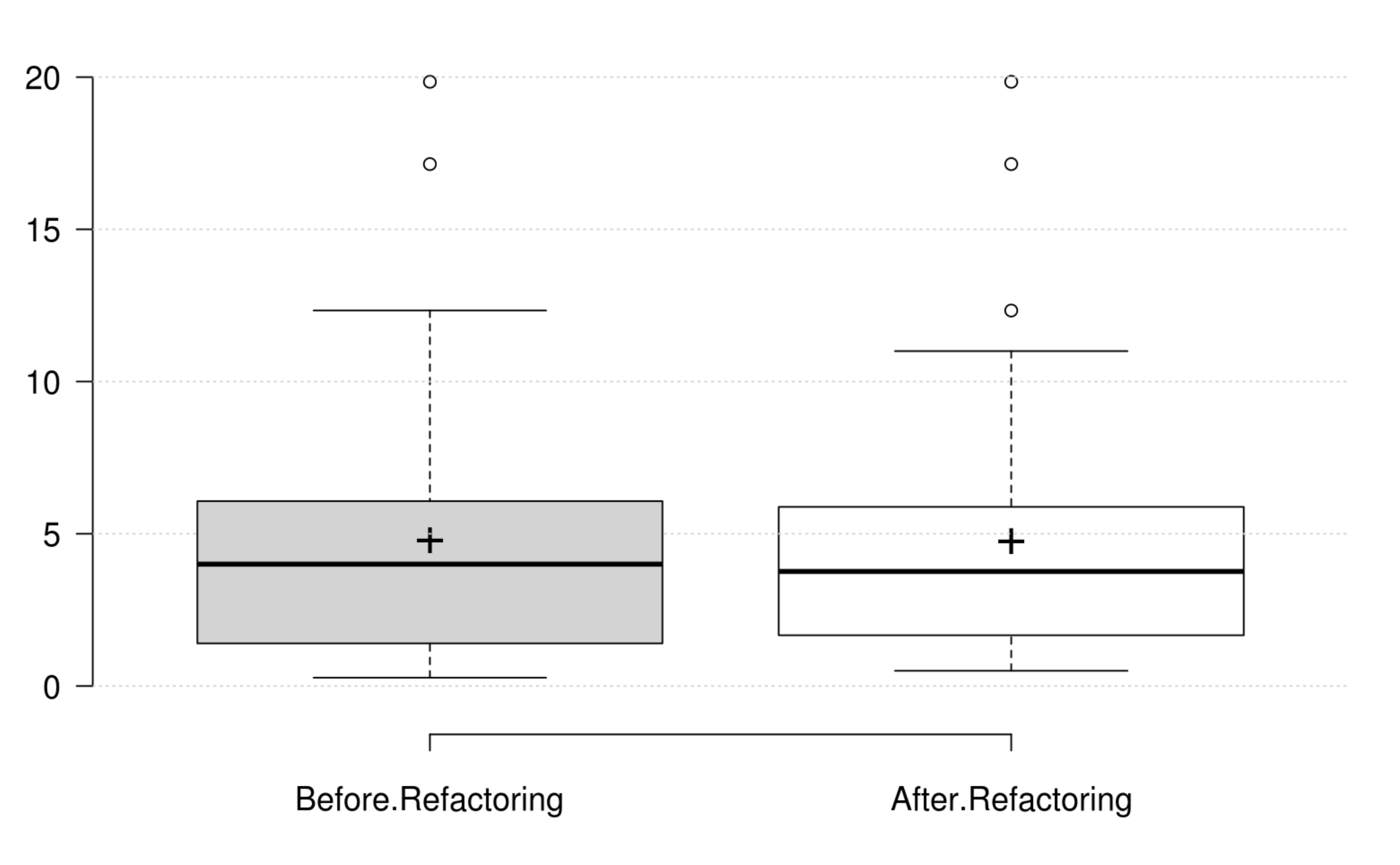
Inheritance: DIT generally decreases as developer intends to improve inheritance, and its variation is significant. IFANIN exhibit opposite variations to inheritance, but it is not statistically significant. Furthermore, our empirical investigation discards NOC from being an indicator for inheritance. Finally, at least one metric has a significant positive variation which matches the developer's perception of improving inheritance.
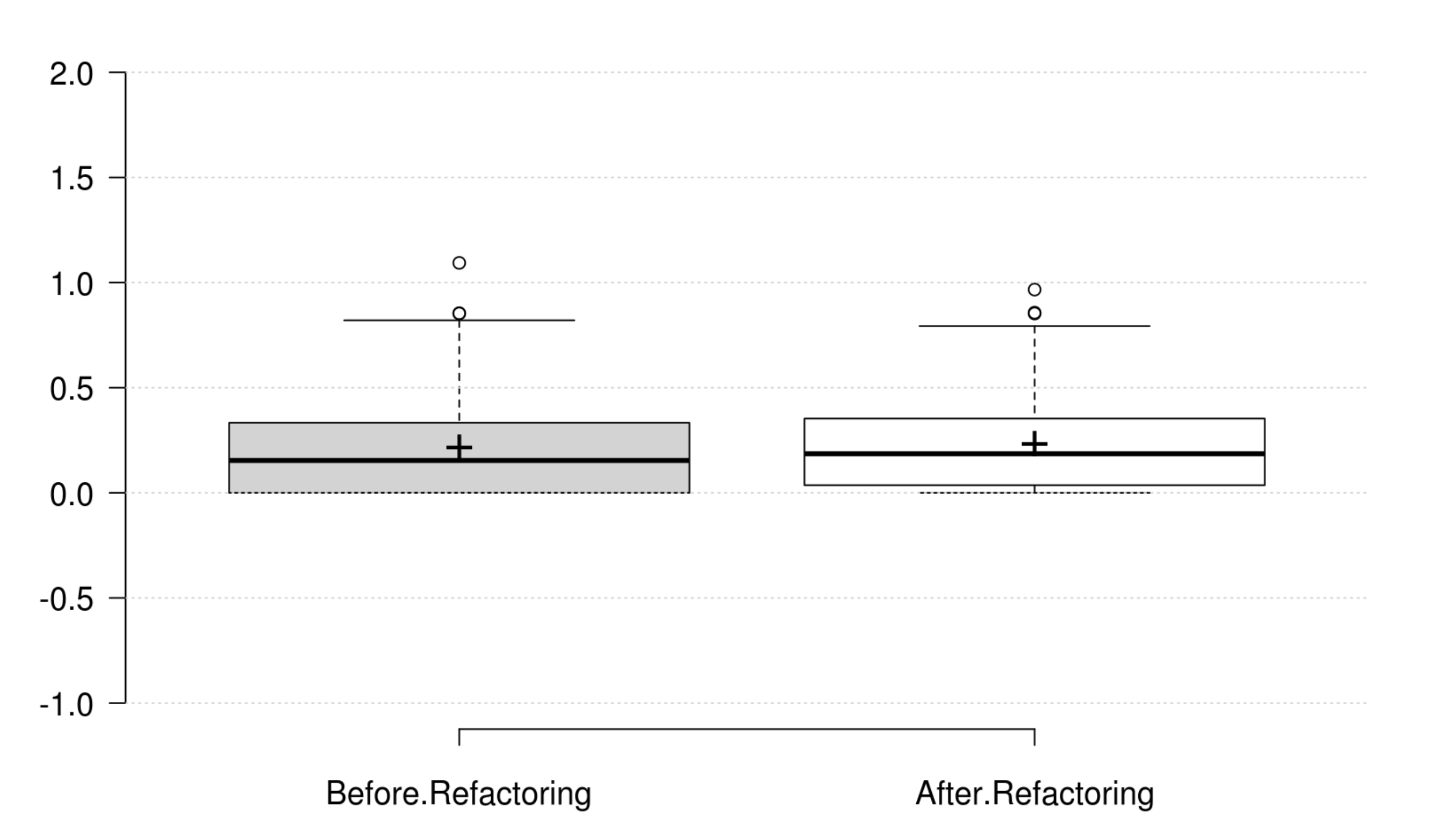
Polymorphism: WMC and RFC exhibit opposite variations to polymorphism, but they are not statistically significant. Therefore, we could not find any metric that has a significant positive variation which matches the developer's perception of improving polymorphism.
Encapsulation: WMC and the normalized LCOM generally decrease as developer intends to improve encapsulation, but their variations are not significant. Therefore, we could not find any metric that has a significant positive variation which matches the developer's perception of improving encapsulation.
Abstraction: WMC and the normalized LCOM generally decrease as developer intends to improve abstraction, but their variations are not significant. Therefore, we could not find any metric that has a significant positive variation which matches the developer's perception of improving abstraction.
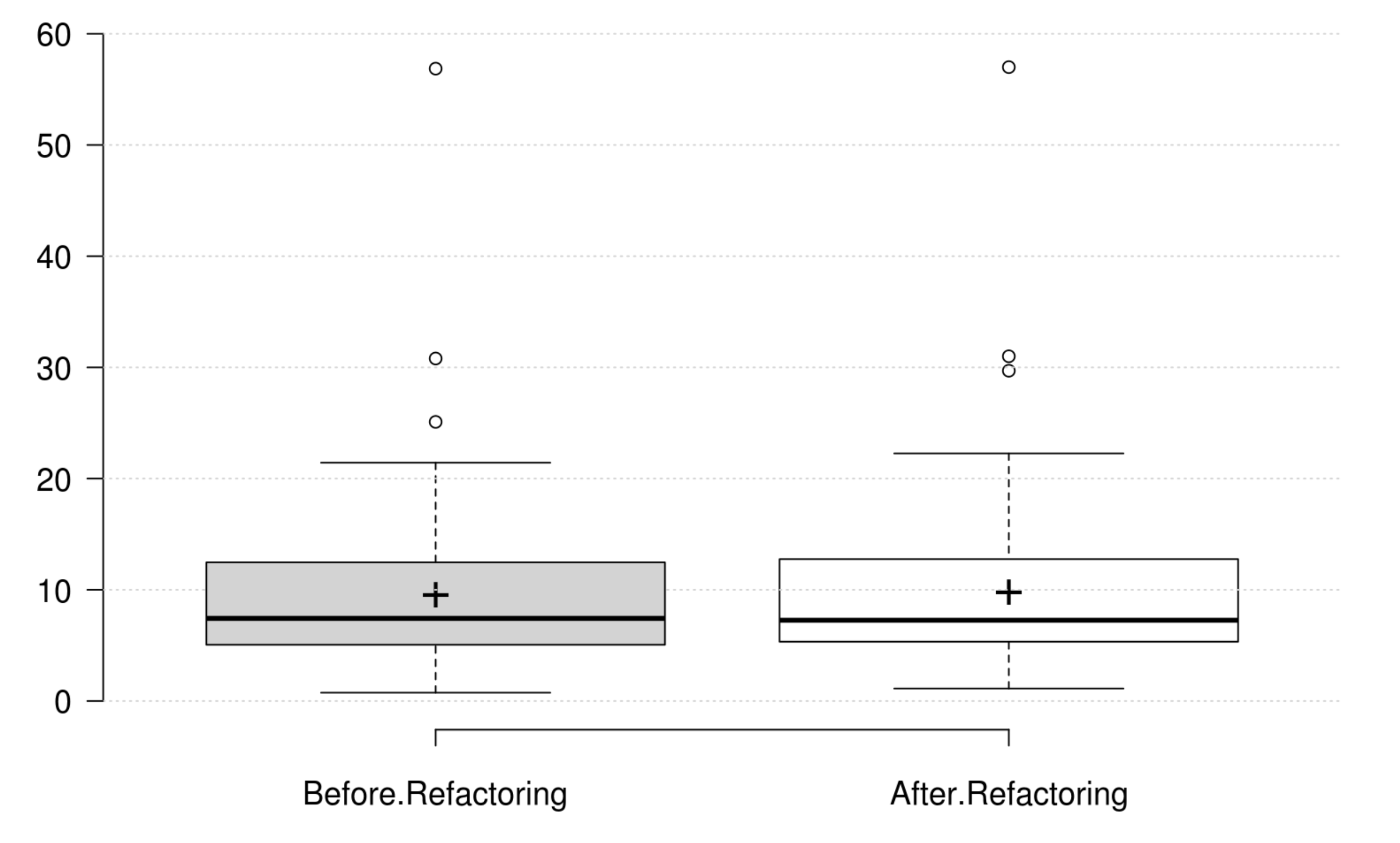
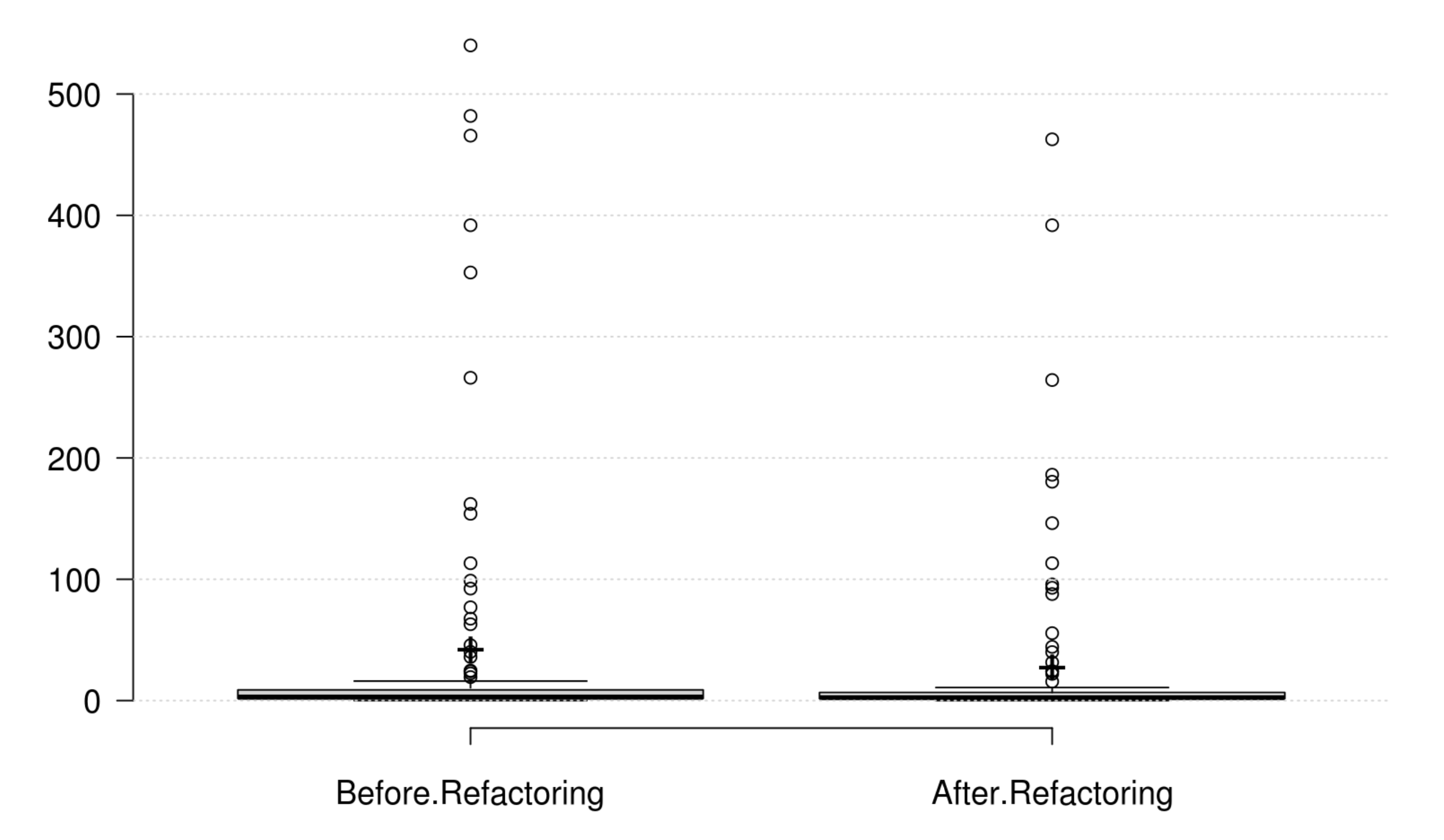
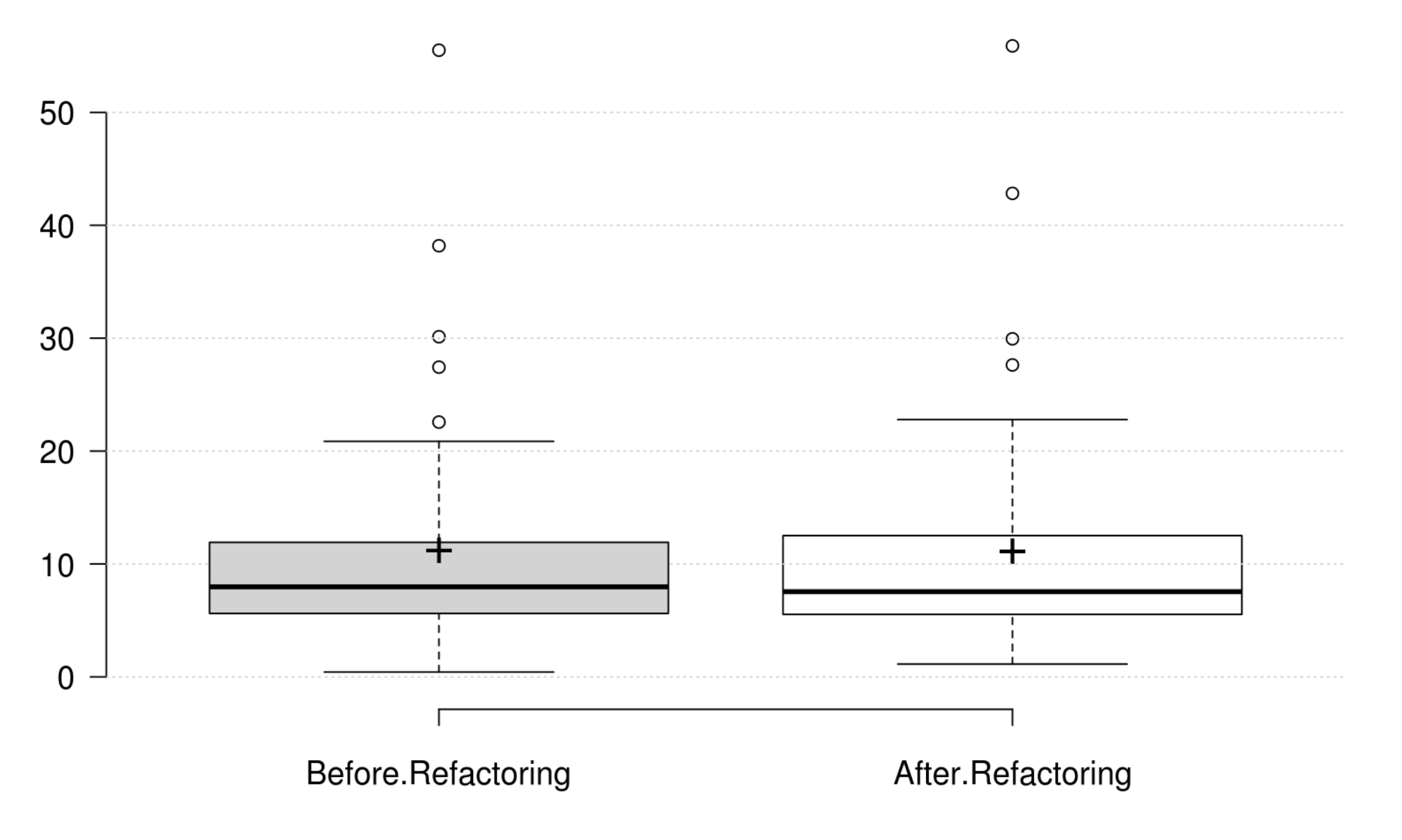
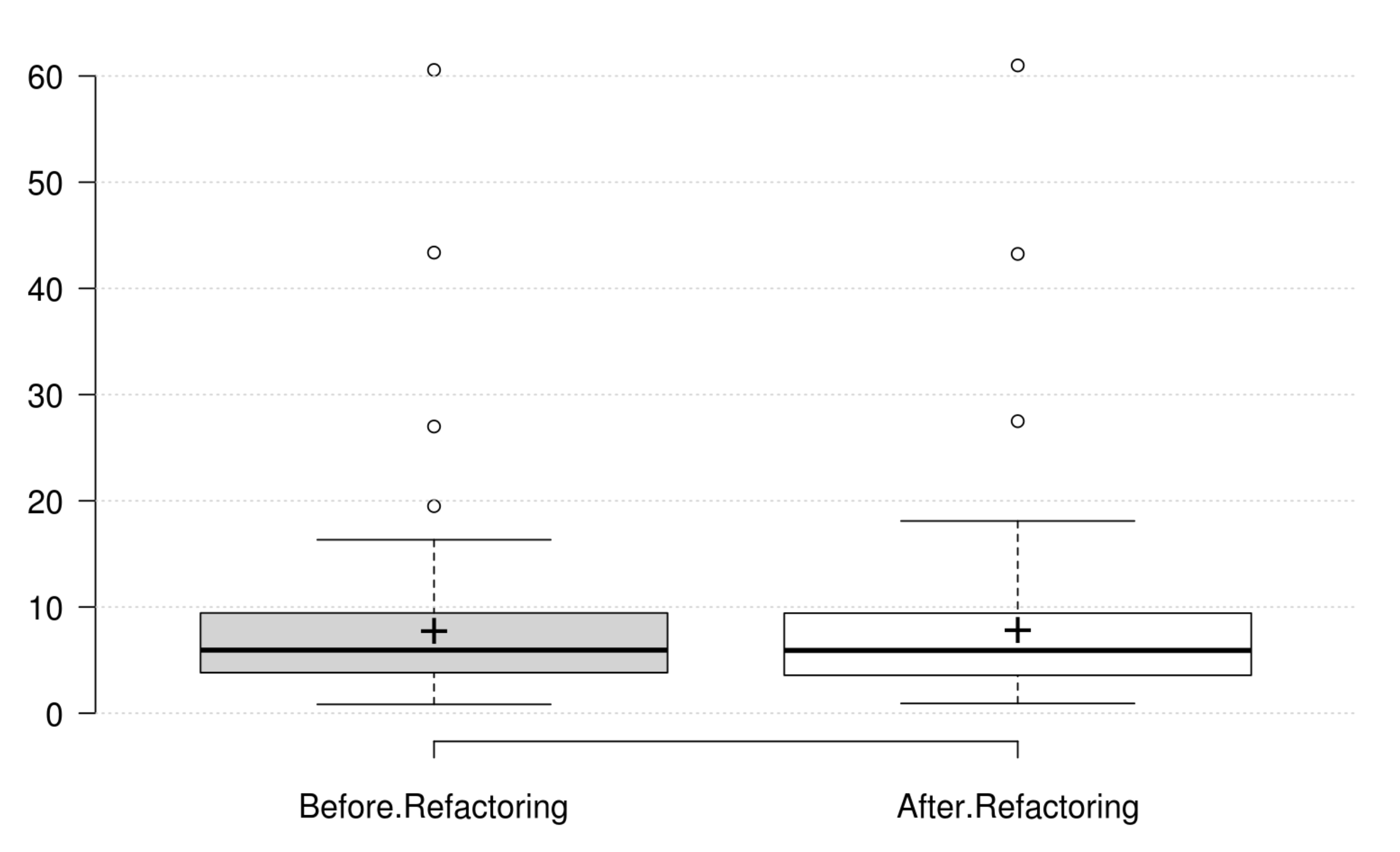
Design Size: CLOC, CDL, NIV, and NIM generally decrease as developer intends to improve design size, but their variations are not significant. Therefore, we could not find any metric that has a significant positive variation which matches the developer's perception of improving design size.