How to refactor this code? An exploratory study on developer-ChatGPT refactoring conversations
Large Language Models (LLMs), like ChatGPT, have gained wide- spread popularity and usage in various software engineering tasks, including refactoring, testing, code review, and program compre- hension. Despite recent studies delving into refactoring documen- tation in commit messages, issues, and code review, little is known about how developers articulate their refactoring needs when in- teracting with ChatGPT. In this paper, our aim is to explore the developer-ChatGPT refactoring conversations to better understand what developers identify areas for improvement in code and how ChatGPT addresses developers’ needs. Our approach relies on text mining refactoring-related conversations from 17,913 ChatGPT prompts and responses, and investigating developers’ explicit refac- toring intention. Our results reveal that (1) developer-ChatGPT con- versations commonly involve generic and specific terms/phrases; (2) developers often make generic refactoring requests, while ChatGPT typically includes the refactoring intention; and (3) various learning settings when prompting ChatGPT in the context of refactoring. We envision that our findings contribute to a broader understanding of the collaboration between developers and AI models in the context of code refactoring, with implications for model improvement, tool development, and best practices in software engineering.
If you are interested to learn more about the process we followed, please refer to our paper.
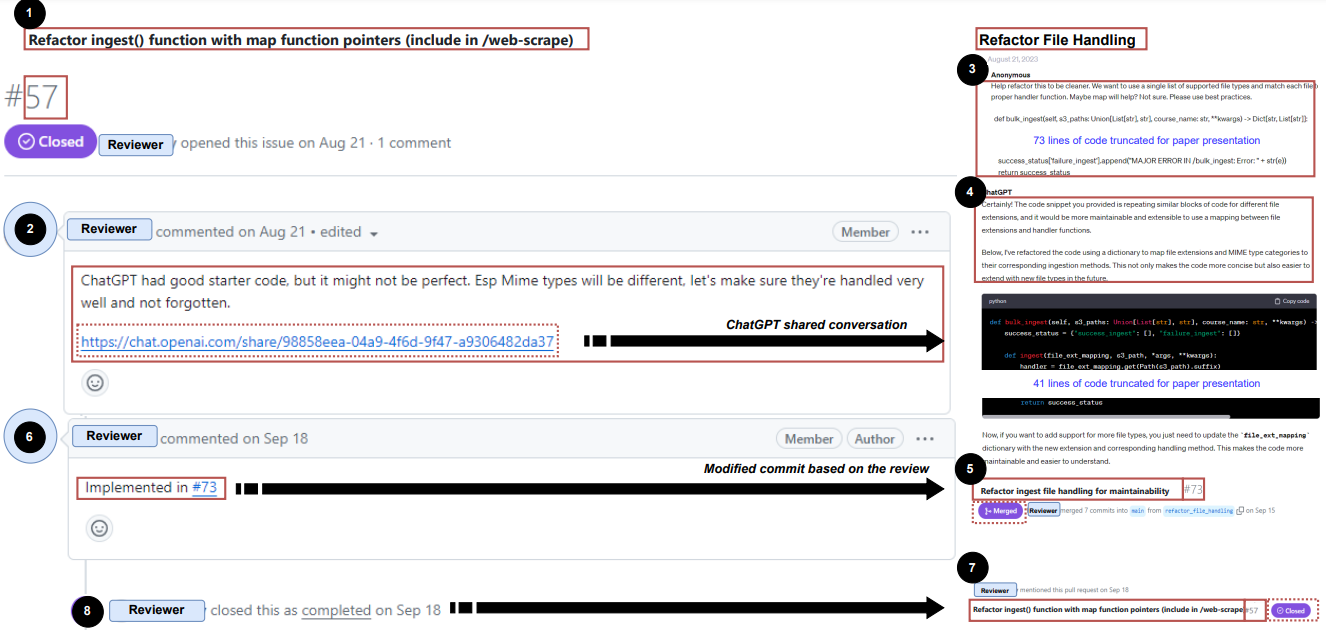
Example of a ChatGPT conversation in the context of improving internal quality attributes
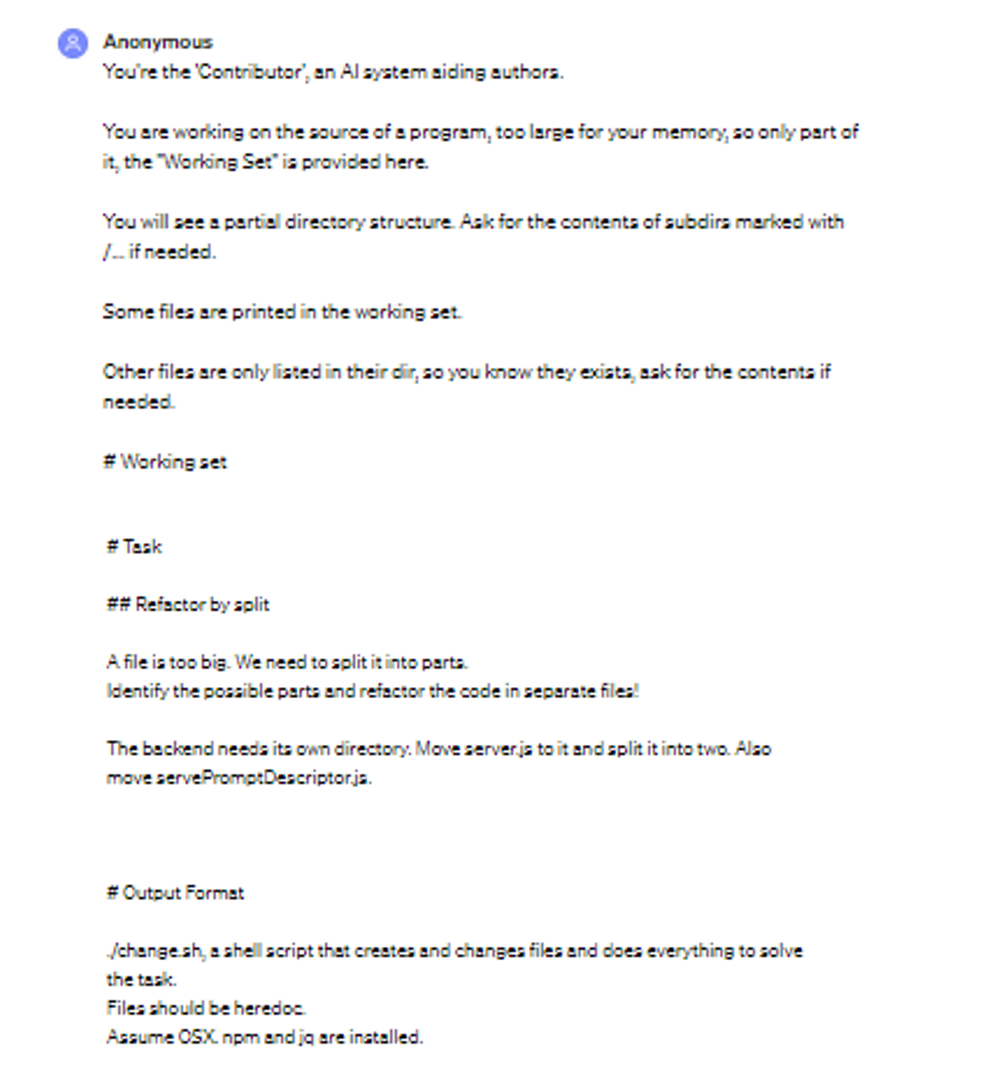
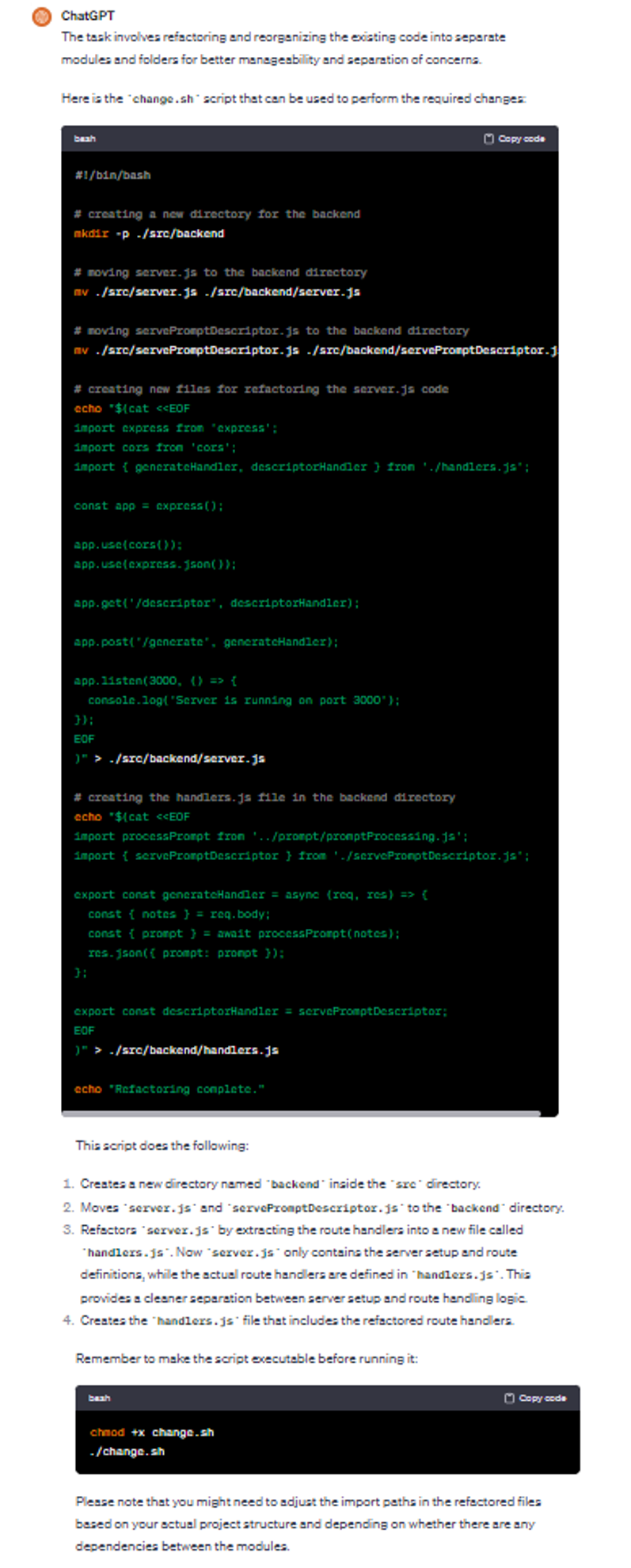
Example of a ChatGPT conversation in the context of improving external quality attributes

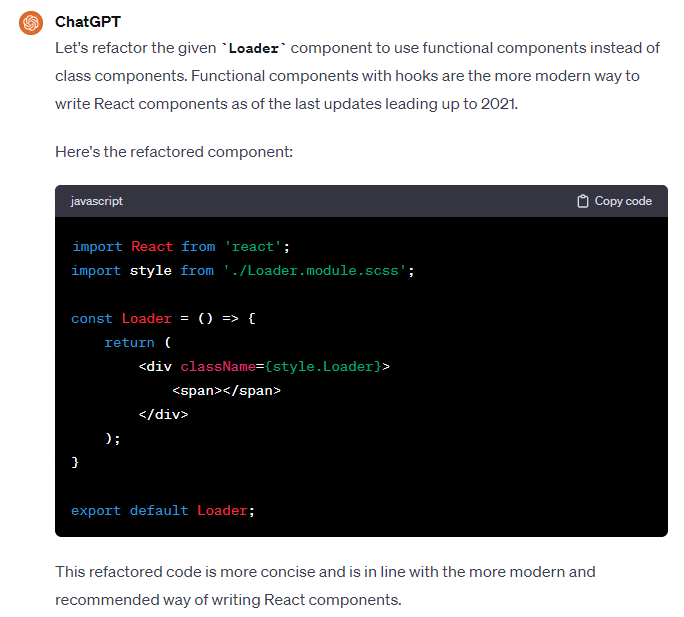
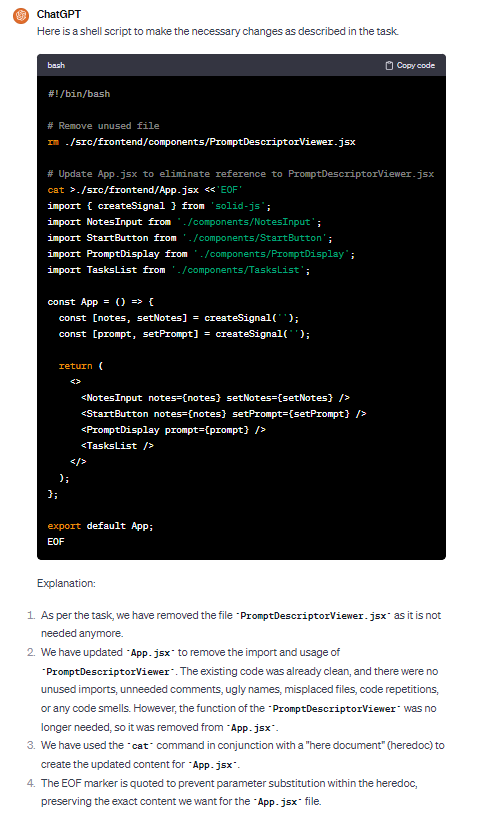
Example of a ChatGPT conversation in the context of removing code smells