
PhD defended!
Congratulations Dr. Eman Abdullah AlOmar for successfully defending your Ph.D. thesis! Her work on understanding developers' perception of refactoring has been published in several venues (ICSE, FSE, ESEM, JSS, IST, ESWA...). You’ve worked hard, come far, and finally PHinisheD! You made everyone proud of you!

MSR 2022
Eman presenting her MSR technical paper about review of refactored code
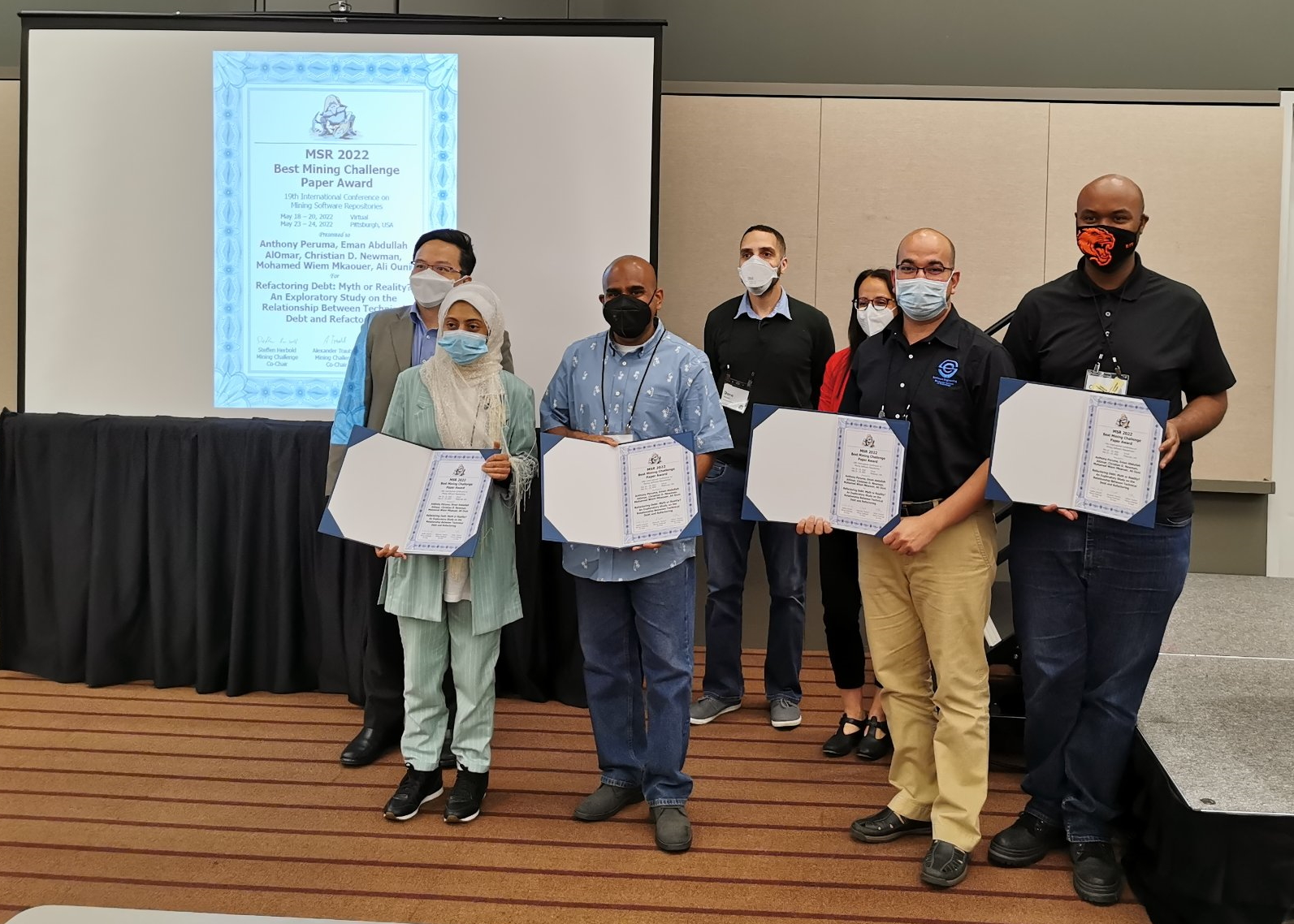

MSR 2022
4 (+1 missing) authors, 4 countries, 4 universities, 1 spiRIT. We got the Mining Challenge best paper award!